Oral contraceptives after myomectomy: a short term trial
- PMID: 19946429
- PMCID: PMC2778449
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/476897
Oral contraceptives after myomectomy: a short term trial
Abstract
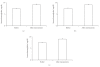
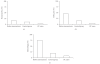
Following myomectomy the rate of fertility is restored and pregnancy may be attempted with a good outcome. In the present study a 3 month treatment with OCs in a group of women after a myomectomy was evaluated. The drug compliance and side effects, the benefits of OC in order to reduce symptoms, to increase post-surgical hemoglobin levels and to avoid an early pregnancy after myomectomy were analyzed. A group of women (n = 55) each with myoma >/=5 cm was recruited: they presented menorrhagia, pelvic pain, dyspareunia and dysmenorrhae. After laparotomic myomectomy the women were divided into 3 groups. Group 1: women (n = 16) treated with pill A (15 mcg of ethynilestradiol + 60 mcg of gestodene); group 2: women (n = 23) treated with pill B (20 mcg of ethynilestradiol + 100 mcg of levonorgestrel); group 3: women (n = 16) treated with a placebo (oral calcium). After three months from myomectomy and treatment patients in each group reported a reduced menorrhagia, dismenorrhea and pelvic pain. Serum haemoglobin levels increased in all women (P < .05). No pregnancy occurred in any group and the compliance was good. A post surgery treatment by using oral contraceptives guarentees pregnancy prevention, associated with reduction of pain, and improvement of haematologic conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Goldman MB, et al. A prospective study of reproductive factors and oral contraceptive use in relation to the risk of uterine leiomyomata. Fertility and Sterility. 1998;70(3):432–439. - PubMed
-
- Parazzini F, La Vecchia C, Negri E, Cecchetti G, Fedele L. Epidemiologic characteristics of women with uterine fibroids: a case-control study. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1988;72(6):853–857. - PubMed
-
- Marshall LM, Spiegelman D, Barbieri RL, et al. Variation in the incidence of uterine leiomyoma among premenopausal women by age and race. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1997;90(6):967–973. - PubMed
-
- Romieu I, Walker AM, Jick S. Determinants of uterine fibroids. Post Marketing Surveillance. 1991;5(2):119–133.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

