Acute myelogenous leukemia switch lineage upon relapse to acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report
- PMID: 19946525
- PMCID: PMC2783110
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-2-154
Acute myelogenous leukemia switch lineage upon relapse to acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report
Abstract
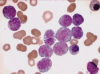
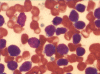
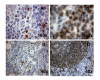
Acute leukemia, the most common form of cancer in children, accounts for approximately 30% of all childhood malignancies, with acute lymphoblastic leukemia being five times more frequent than acute myeloid leukemia. Lineage switch is the term that has been used to describe the phenomenon of acute leukemias that meet the standard French-American-British system criteria for a particular lineage (either lymphoid or myeloid) upon initial diagnosis, but meet the criteria for the opposite lineage at relapse. Many reports have documented conversions of acute lymphoblastic leukemia to acute myeloid leukemia. Here, we report the case of a 4-year-old child with acute myeloid leukemia, which upon relapse switched to acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The morphologic, phenotypic, and molecular features suggest the origin of a new leukemic clone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lineage switch of acute myeloid leukemia to T-Cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia - A unique case report.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2023 Jan-Mar;66(1):191-195. doi: 10.4103/ijpm.ijpm_441_21. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36656240
-
Lineage switch at relapse of childhood acute leukemia: a report of four cases.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Jun;26(6):829-31. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.6.829. Epub 2011 May 18. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21655072 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage switch in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer. 1994 Mar 1;73(5):1526-32. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19940301)73:5<1526::aid-cncr2820730534>3.0.co;2-e. Cancer. 1994. PMID: 8111722
-
To B- or not to B-: A review of lineage switched acute leukemia.Int J Lab Hematol. 2022 Sep;44 Suppl 1:64-70. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13923. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Int J Lab Hematol. 2022. PMID: 35770493 Review.
-
Childhood and adolescent lymphoid and myeloid leukemia.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004:118-45. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2004.1.118. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2004. PMID: 15561680 Review.
Cited by
-
Lineage switching in acute leukemias: a consequence of stem cell plasticity?Bone Marrow Res. 2012;2012:406796. doi: 10.1155/2012/406796. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Bone Marrow Res. 2012. PMID: 22852088 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and Microenvironmental Regulation of Lineage Ambiguity in Leukemia.Front Oncol. 2017 Nov 6;7:268. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00268. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29164065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of therapy-related acute lymphoblastic leukemia following the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.Leuk Res Rep. 2022 Mar 1;17:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.lrr.2022.100297. eCollection 2022. Leuk Res Rep. 2022. PMID: 35284228 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing dynamics and clonal heterogeneity of Cbx7-induced leukemic stem cells by cellular barcoding.Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Jan 13;4(1):74-89. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Stem Cell Reports. 2015. PMID: 25434821 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroleukemia relapsing as precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia.Korean J Lab Med. 2011 Apr;31(2):81-5. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.2.81. Korean J Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21474980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith OP, Hann IM. In: Pediatric Hematology. 3. Arceci RJ, Hann IM, Smith OP, editor. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2006. Clinical features and therapy of lymphoblastic leukemia; pp. 450–481.
-
- Golub TR, Arceci RJ. Principles and practice of pediatric oncology. 5. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia; 2006. Acute Myelogenous Leukemia; pp. 591–644.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

