Missed diagnosis of ankle pseudoaneurysm following ankle arthroscopy: a case report
- PMID: 19946533
- PMCID: PMC2783118
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-2-162
Missed diagnosis of ankle pseudoaneurysm following ankle arthroscopy: a case report
Abstract
Background: Pseudoaneurysm formation is rare complication after arthroscopy with incidence of 0.008%, easy to misdiagnose. Its potential catastrophic sequelae should not be underestimated.
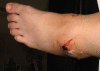
Case presentation: We present a case of missed diagnosis of traumatic anterior tibial artery pseudoaneurysm in a 39 years old female, instead treated as post operative arthroscopy infection. The diagnosis was confirmed with a duplex ultrasound scan and referred to the vascular surgeon with successful out come.
Conclusion: In view of rare presentation this complication, it is easily missed. According to one study, incidence of anatomic variations of anterior tibial artery range from 2.4 to 12%. Because of this anatomical variation in course along with other factors, pseudoaneurysm formation at ankle is relatively high. In this report, we discuss the diagnosis, anatomical variations of anterior tibial artery and prevention of this complication following arthroscopy. We believe that surgeons operating in this region should take into account these anatomical variations preoperatively.
Figures
References
-
- Mariani PP, Mancini L, Giorgini TL. Pseudoaneurysm as a complication of ankle arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2001;17:400–402. - PubMed
-
- Darwish A, Ehsan O, Marynissen H, Al-Khaffaf H. Pseudoaneurysm of the anterior tibial artery after ankle arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2004;20:e63–64. - PubMed
-
- O'Farrell D, Dudeney S, McNally S, Moran R. Pseudoaneurysm formation after ankle arthroscopy. Foot Ankle Int. 1997;18:578–579. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources