Circumferential thoracolumbar corrective fusion with an anterior interbody fresh-frozen femoral head allograft for osteoporotic lower acute kyphosis: a case report
- PMID: 19946544
- PMCID: PMC2783067
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-3-137
Circumferential thoracolumbar corrective fusion with an anterior interbody fresh-frozen femoral head allograft for osteoporotic lower acute kyphosis: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Lower acute kyphosis (LAK) is a postural deformity caused by severe osteoporotic vertebral collapse at the thoracolumbar junction. Corrective surgery is indicated for severe cases, but no case report using a fresh-frozen femoral head allograft was found in the English literature.
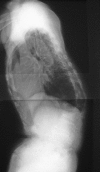
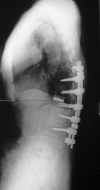
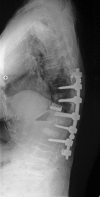
Case presentation: A 69-year-old Japanese woman with severe LAK with osteoporotic vertebral fractures from T11 to L2 complained of severe back pain and difficulty in walking. The rigid kyphosis measured 74 degrees from T10 to L3. The patient underwent an anterior release and interbody fusion using a fresh-frozen femoral head allograft (T11-L3) and a posterior instrumented fusion (T10-L3). Postoperatively, kyphosis was corrected to 28 degrees , and the patient's symptoms were alleviated. The allograft bone was fully incorporated 1 year postoperatively. A new vertebral fracture at T10 occurred after 2 years, resulting in a slight loss of correction. A kyphosis angle of 35 degrees at 2 years was maintained at 12 years (age, 81 years). She remained free of back pain and able to walk without a cane over the 12-year follow-up.
Conclusion: For treatment of severe osteoporotic LAK, anterior reconstruction is essential to obtain good spinal alignment and prevent recurrence. A fresh-frozen femoral head allograft, in combination with rigid posterior instrumented fixation, fulfills this function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Surgical choice of posterior osteotomy way for senile osteoporotic thoracolumbar fracture with kyphosis].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020 Feb 25;33(2):121-6. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.2020.02.006. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020. PMID: 32133809 Chinese.
-
[Effectiveness of long segment fixation combined with vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;27(11):1331-7. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24501892 Chinese.
-
[Clinical features and strategies for treatment of spinal fracture complicating ankylosing spondylitis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Nov 6;87(41):2893-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18261302 Chinese.
-
Simultaneous posterior and anterior approaches with posterior vertebral wall preserved for rigid post-traumatic kyphosis in thoracolumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Aug 1;37(17):E1085-91. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318255e353. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22460924
-
Anterolateral Corrective Lumbar Corpectomy and Interbody Fusion by Using Extended Screw Fixation without Posterior Instrumentation for Posttraumatic Kyphosis.Case Rep Orthop. 2013;2013:614757. doi: 10.1155/2013/614757. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Case Rep Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23970987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaneda K, Asano S, Hashimoto T, Satoh S, Fujiya M. The treatment of osteoporotic-posttraumatic vertebral collapse using the Kaneda device and a bioactive ceramic vertebral prosthesis. Spine. 1992;17(8 Suppl):S295–303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

