Synthesis and Structures of Dimeric Iron(III)-Oxo and -Imido Complexes Containing Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds
- PMID: 19946568
- PMCID: PMC2782865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ica.2006.12.020
Synthesis and Structures of Dimeric Iron(III)-Oxo and -Imido Complexes Containing Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonds
Abstract
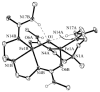
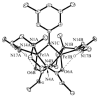
Hydrogen bonding networks proximal to metal centers are emerging as a viable means for controlling secondary coordination spheres. This has led to the regulation of reactivity and isolation of complexes with new structural motifs. We have used the tridenate ligand bis[(N'-tert-butylureido)-N-ethyl]-N-methylaminato ([H(2)1](2-)) that contains two hydrogen bond donors to examine the oxidation of the Fe(II)-acetate complex, [Fe(II)H(2)1(η(2)-OAc)](-) with dioxygen, amine N-oxides, and xylyl azide. A complex with Fe(III)-O-Fe(III) core results from the oxidation with dioxygen and amine N-oxides, in which the oxo ligand is involved in hydrogen bonding to the [H(2)1](2-) ligand. A distinctly different hydrogen bonding network was found in Fe(III) dimer isolated from the reaction with the xylyl azide: a rare Fe(III)-N(R)-Fe(III) core was observed that does not have hydrogen bonds to the bridging nitrogen atom. The intramolecular H-bond networks within these dimers appear to adjust to the presence of the bridging species and rearrange to its size and electron density.
Figures
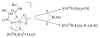
Similar articles
-
A modular approach toward regulating the secondary coordination sphere of metal ions: differential dioxygen activation assisted by intramolecular hydrogen bonds.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Dec 6;128(48):15476-89. doi: 10.1021/ja063935+. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 17132015
-
Utilization of hydrogen bonds to stabilize M-O(H) units: synthesis and properties of monomeric iron and manganese complexes with terminal oxo and hydroxo ligands.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Mar 3;126(8):2556-67. doi: 10.1021/ja0305151. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 14982465
-
Structural diversity in manganese, iron and cobalt complexes of the ditopic 1,2-bis(2,2'-bipyridyl-6-yl)ethyne ligand and observation of epoxidation and catalase activity of manganese compounds.Dalton Trans. 2010 Aug 21;39(31):7266-75. doi: 10.1039/b925129d. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Dalton Trans. 2010. PMID: 20582360
-
Manganese-Oxygen Intermediates in O-O Bond Activation and Hydrogen-Atom Transfer Reactions.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Nov 21;50(11):2706-2717. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00343. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 29064667 Review.
-
Electronic structure and reactivity of three-coordinate iron complexes.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Aug;41(8):905-14. doi: 10.1021/ar700267b. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 18646779 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Three-coordinate terminal imidoiron(III) complexes: structure, spectroscopy, and mechanism of formation.Inorg Chem. 2010 Jul 5;49(13):6172-87. doi: 10.1021/ic100846b. Inorg Chem. 2010. PMID: 20524625 Free PMC article.
-
A structure and reactivity analysis of monomeric Ni(II)-hydroxo complexes prepared from water.Dalton Trans. 2009 Apr 28;(16):2986-92. doi: 10.1039/b820209e. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Dalton Trans. 2009. PMID: 19352526 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Iron-Imido Species Relevant for N-Group Transfer Chemistry.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Feb 17;138(6):1983-93. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12582. Epub 2016 Feb 4. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 26788747 Free PMC article.
-
Lewis Base-Enhanced C-H Bond Functionalization Mediated by a Diiron Imido Complex.Inorg Chem. 2025 Feb 10;64(5):2217-2231. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.4c03922. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Inorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 39854679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen MP, Mehn MP, Que L., Jr Angew Chem Int Ed. 2003;42:4357. - PubMed
- Feichtinger D, Plattner DA. Chem Eur J. 2001;7:591. - PubMed
- Du Bois J, Tomooka CS, Hong J, Carreira EM. Acc Chem Res. 1997;30:364.
- Groves JT, Lee J, Marla SS. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:6229.
- Brandt P, Södergren MJ, Anderson PG, Norrby PO. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:8013.
-
- Wigley DE. Prog Inorg Chem. 1994;42:239.
- Eikey RA, Abu-Omar MM. Coord Chem Rev. 2003;243:83.
-
-
Recent examples:
- Mindiola DJ, Hillhouse GL. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:4623. - PubMed
- Jenkins DM, Betley TA, Peters JC. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:11238. - PubMed
- Thyagarajan S, Shay DT, Incarvito CD, Rheingold AL, Theopold KH. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:4440. - PubMed
- Eikey RA, Khan SI, Abu-Omar MM. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2002;41:3592. - PubMed
- Dai X, Kapoor P, Warren TH. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:4798. - PubMed
- Thomas CM, Mankad NP, Peters JC. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:4957. - PMC - PubMed
- Jenson MP, Mehn MP, Que L., Jr Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2003;42:4357. - PubMed
- Nazif AK, Nazif TN, Achim C, Lee SC. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:11013.
-
-
- Borovik AS. Acc Chem Res. 2005;38:54. references therein. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
