Accomplishments in genome-scale in silico modeling for industrial and medical biotechnology
- PMID: 19946878
- PMCID: PMC3160784
- DOI: 10.1002/biot.200900234
Accomplishments in genome-scale in silico modeling for industrial and medical biotechnology
Abstract
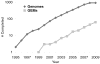
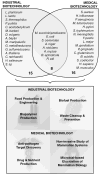
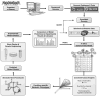
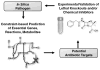
Driven by advancements in high-throughput biological technologies and the growing number of sequenced genomes, the construction of in silico models at the genome scale has provided powerful tools to investigate a vast array of biological systems and applications. Here, we review comprehensively the uses of such models in industrial and medical biotechnology, including biofuel generation, food production, and drug development. While the use of in silico models is still in its early stages for delivering to industry, significant initial successes have been achieved. For the cases presented here, genome-scale models predict engineering strategies to enhance properties of interest in an organism or to inhibit harmful mechanisms of pathogens. Going forward, genome-scale in silico models promise to extend their application and analysis scope to become a trans-formative tool in biotechnology.
Figures
References
-
- Schilling CH, Palsson BO. Assessment of the metabolic capabilities of Haemophilus influenzae Rd through a genome-scale pathway analysis. J Theor Biol. 2000;203:249–283. - PubMed
-
- Covert MW, Schilling CH, Palsson B. Regulation of gene expression in flux balance models of metabolism. J Theor Biol. 2001;213:73–88. - PubMed
-
- Covert MW, Knight EM, Reed JL, Herrgard MJ, Palsson BO. Integrating high-throughput and computational data elucidates bacterial networks. Nature. 2004;429:92–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

