Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes
- PMID: 19948051
- PMCID: PMC2792220
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-148
Regulation of the IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 genes by the microRNAs miR-140 and miR-27a in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes
Abstract
Background: MMP-13 and IGFBP-5 are important factors involved in osteoarthritis (OA). We investigated whether two highly predicted microRNAs (miRNAs), miR-140 and miR-27a, regulate these two genes in human OA chondrocytes.
Methods: Gene expression was determined by real-time PCR. The effect of each miRNA on IGFBP-5 and MMP-13 expression/production was evaluated by transiently transfecting their precursors (pre-miRNAs) and inhibitors (anti-miRNAs) into human OA chondrocytes. Modulation of IGFBP-5, miR-140 and miR-27a expression was determined upon treatment of OA chondrocytes with cytokines and growth factors.
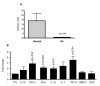
Results: IGFBP-5 was expressed in human chondrocytes with its level significantly lower (p < 0.04) in OA. Five computational algorithms identified miR-140 and miR-27a as possible regulators of MMP-13 and IGFBP-5 expression. Data showed that both miRNAs were expressed in chondrocytes. There was a significant reduction (77%, p < 0.01) in miR-140 expression in OA compared to the normal chondrocytes, whereas miR-27a expression was only slightly decreased (23%). Transfection with pre-miR-140 significantly decreased (p = 0.0002) and with anti-miR-140 significantly increased (p = 0.05) IGFBP-5 expression at 24 hours, while pre-miR-27a did not affect either MMP-13 or IGFBP-5. Treatment with anti-miR-27a, but not with anti-miR-140, significantly increased the expression of both MMP-13 (p < 0.05) and IGFBP-5 (p < 0.01) after 72 hours of incubation. MMP-13 and IGFBP-5 protein production followed the same pattern as their expression profile. These data suggest that IGFBP-5 is a direct target of miR-140, whereas miR-27a down-regulates, likely indirectly, both MMP-13 and IGFBP-5.
Conclusion: This study is the first to show the regulation of these miRNAs in human OA chondrocytes. Their effect on two genes involved in OA pathophysiology adds another level of complexity to gene regulation, which could open up novel avenues in OA therapeutic strategies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrostatic Pressure Regulates MicroRNA Expression Levels in Osteoarthritic Chondrocyte Cultures via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 12;18(1):133. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010133. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28085114 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-602 and microRNA-608 regulate sonic hedgehog expression via target sites in the coding region in human chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Feb;67(2):423-34. doi: 10.1002/art.38952. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25385442 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-127-5p regulates matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and interleukin-1β-induced catabolic effects in human chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Dec;65(12):3141-52. doi: 10.1002/art.38188. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 24022470
-
MicroRNA in osteoarthritis: physiopathology, diagnosis and therapeutic challenge.Br Med Bull. 2019 Jun 19;130(1):137-147. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldz015. Br Med Bull. 2019. PMID: 31066454
-
The Involvement of MicroRNAs in Osteoarthritis and Recent Developments: A Narrative Review.Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2018 Jun 29;29(2):67-79. doi: 10.31138/mjr.29.2.67. eCollection 2018 Jun. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 32185303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the Microenvironment in Controlling the Fate of Bioprinted Stem Cells.Chem Rev. 2020 Oct 14;120(19):11056-11092. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00126. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Chem Rev. 2020. PMID: 32558555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-140 is a negative feedback regulator of MMP-13 in IL-1β-stimulated human articular chondrocyte C28/I2 cells.Inflamm Res. 2012 May;61(5):503-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0438-6. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22273691
-
E2 regulates MMP-13 via targeting miR-140 in IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degradation in human chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 May 10;18(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0997-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27165343 Free PMC article.
-
RNA sequencing data integration reveals an miRNA interactome of osteoarthritis cartilage.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Feb;78(2):270-277. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213882. Epub 2018 Dec 1. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30504444 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic and microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis, and osteoarthritis.Trends Mol Med. 2012 Feb;18(2):109-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.11.005. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Trends Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22178468 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Billinghurst RC, Dahlberg L, Ionescu M, Reiner A, Bourne R, Rorabeck C, Mitchell P, Hambor J, Diekmann O, Tschesche H, Chen J, Van Wart H, Poole AR. Enhanced cleavage of Type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:1534–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI119316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mitchell PG, Magna HA, Reeves LM, Lopresti-Morrow LL, Yocum SA, Rosner PJ, Geoghegan KF, Hambor JE. Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1996;97:761–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI118475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

