DNA microarray profiling of genes differentially regulated by the histone deacetylase inhibitors vorinostat and LBH589 in colon cancer cell lines
- PMID: 19948057
- PMCID: PMC2799439
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-2-67
DNA microarray profiling of genes differentially regulated by the histone deacetylase inhibitors vorinostat and LBH589 in colon cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: Despite the significant progress made in colon cancer chemotherapy, advanced disease remains largely incurable and novel efficacious chemotherapies are urgently needed. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) represent a novel class of agents which have demonstrated promising preclinical activity and are undergoing clinical evaluation in colon cancer. The goal of this study was to identify genes in colon cancer cells that are differentially regulated by two clinically advanced hydroxamic acid HDACi, vorinostat and LBH589 to provide rationale for novel drug combination partners and identify a core set of HDACi-regulated genes.
Methods: HCT116 and HT29 colon cancer cells were treated with LBH589 or vorinostat and growth inhibition, acetylation status and apoptosis were analyzed in response to treatment using MTS, Western blotting and flow cytometric analyses. In addition, gene expression was analyzed using the Illumina Human-6 V2 BeadChip array and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.
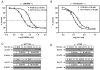
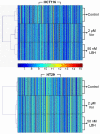
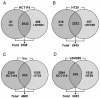
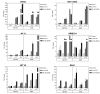
Results: Treatment with either vorinostat or LBH589 rapidly induced histone acetylation, cell cycle arrest and inhibited the growth of both HCT116 and HT29 cells. Bioinformatic analysis of the microarray profiling revealed significant similarity in the genes altered in expression following treatment with the two HDACi tested within each cell line. However, analysis of genes that were altered in expression in the HCT116 and HT29 cells revealed cell-line-specific responses to HDACi treatment. In addition a core cassette of 11 genes modulated by both vorinostat and LBH589 were identified in both colon cancer cell lines analyzed.
Conclusion: This study identified HDACi-induced alterations in critical genes involved in nucleotide metabolism, angiogenesis, mitosis and cell survival which may represent potential intervention points for novel therapeutic combinations in colon cancer. This information will assist in the identification of novel pathways and targets that are modulated by HDACi, providing much-needed information on HDACi mechanism of action and providing rationale for novel drug combination partners. We identified a core signature of 11 genes which were modulated by both vorinostat and LBH589 in a similar manner in both cell lines. These core genes will assist in the development and validation of a common gene set which may represent a molecular signature of HDAC inhibition in colon cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
HDAC gene expression in pancreatic tumor cell lines following treatment with the HDAC inhibitors panobinostat (LBH589) and trichostatine (TSA).Pancreatology. 2012 Mar-Apr;12(2):146-55. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Pancreatology. 2012. PMID: 22487525
-
The HDAC inhibitor LBH589 induces ERK-dependent prometaphase arrest in prostate cancer via HDAC6 inactivation and down-regulation.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 4;8(9):e73401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073401. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023871 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained inhibition of deacetylases is required for the antitumor activity of the histone deactylase inhibitors panobinostat and vorinostat in models of colorectal cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Aug;31(4):845-57. doi: 10.1007/s10637-012-9914-7. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23299388
-
Development of the pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589): successes and challenges.Cancer Lett. 2009 Aug 8;280(2):233-41. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.02.019. Epub 2009 Apr 2. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19344997 Review.
-
Panobinostat for the treatment of multiple myeloma.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 May;21(5):733-47. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.668883. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22404247 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibition of esophageal cancer cells by combination of HDAC inhibitors and Azacytidine.Epigenetics. 2015;10(5):431-45. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1039216. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25923331 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic stem cells and transforming growth factor β in hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Sep;9(9):530-8. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.114. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22710573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs and latent HIV - A search for novel targets for latency reversal.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 11;14(11):e0224879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224879. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31710657 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray gene expression profiling reveals potential mechanisms of tumor suppression by the class I HDAC-selective benzoylhydrazide inhibitors.Genom Data. 2015 Sep 1;5:257-259. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2015.06.019. Genom Data. 2015. PMID: 26217556 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs and Epigenetic Molecular Functions. A Pharmacological Data Scientometric Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7250. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147250. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, Balasis M, Fiskus W, Guo F, Rocha K, Kumaraswamy S, Boyapalle S, Atadja P. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(29):26729–26734. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C500186200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

