Spiperone enhances intracellular calcium level and inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 19948059
- PMCID: PMC2789054
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2210-9-13
Spiperone enhances intracellular calcium level and inhibits the Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Wnt signaling affects fundamental development pathways by regulating cell proliferation and differentiation. Aberrant activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes the development of several cancers and is an attractive target for chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agents.
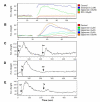
Results: In order to identify the novel antagonists for the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, we employed a cell-based Wnt reporter system (TOPflash) to screen a library of 960 known drugs. We identified spiperone, a psychotropic drug, as a novel Wnt inhibitor, which specifically blocks canonical Wnt signaling prior to the activation of beta-catenin. The Wnt inhibitory function of spiperone is not associated with its dopamine-, serotonin- and sigma-receptor antagonist properties. Instead, spiperone increases intracellular calcium levels in a similar manner to thapsigargin, that also impedes Wnt signal transduction. Inhibition of protein kinase C had no effect on spiperone-mediated antagonism of Wnt signaling.
Conclusion: Spiperone is a calcium regulator. It inhibits Wnt signaling by enhancing intracellular calcium levels.
Figures


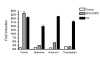

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

