Interaction of heparins and dextran sulfates with a mesoscopic protein nanopore
- PMID: 19948118
- PMCID: PMC2784562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.09.019
Interaction of heparins and dextran sulfates with a mesoscopic protein nanopore
Abstract
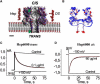
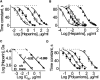
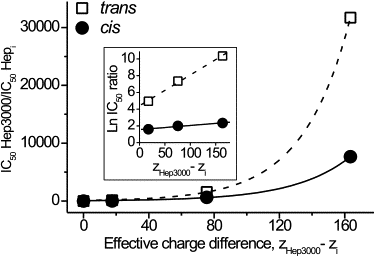
A mechanism of how polyanions influence the channel formed by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin is described. We demonstrate that the probability of several types of polyanions to block the ion channel depends on the presence of divalent cations and the polyanion molecular weight and concentration. For heparins, a 10-fold increase in molecular weight decreases the half-maximal inhibitory concentration, IC(50), nearly 10(4)-fold. Dextran sulfates were less effective at blocking the channel. The polyanions are significantly more effective at reducing the conductance when added to the trans side of this channel. Lastly, the effectiveness of heparins on the channel conductance correlated with their influence on the zeta-potential of liposomes. A model that includes the binding of polyanions to the channel-membrane complex via Ca(2+)-bridges and the asymmetry of the channel structure describes the data adequately. Analysis of the single channel current noise of wild-type and site-directed mutant versions of alpha-hemolysin channels suggests that a single polyanion enters the pore due to electrostatic forces and physically blocks the ion conduction path. The results might be of interest for pharmacology, biomedicine, and research aiming to design mesoscopic pore blockers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The hinge portion of the S. aureus alpha-toxin crosses the lipid bilayer and is part of the trans-mouth of the channel.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997 Oct 2;1329(1):51-60. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(97)00087-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997. PMID: 9370244
-
Imaging alpha-hemolysin with molecular dynamics: ionic conductance, osmotic permeability, and the electrostatic potential map.Biophys J. 2005 Jun;88(6):3745-61. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.058727. Epub 2005 Mar 11. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15764651 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of distant charge reversals within a robust beta-barrel protein pore.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Jul 8;114(26):8750-9. doi: 10.1021/jp101311s. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20540583 Free PMC article.
-
Ion channels and bacterial infection: the case of beta-barrel pore-forming protein toxins of Staphylococcus aureus.FEBS Lett. 2003 Sep 18;552(1):54-60. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00850-0. FEBS Lett. 2003. PMID: 12972152 Review.
-
Staphylococcal pore-forming toxins.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;257:53-83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56508-3_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11417122 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Iron Metabolism at the Interface between Host and Pathogen: From Nutritional Immunity to Antibacterial Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 20;21(6):2145. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062145. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32245010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Channel-forming bacterial toxins in biosensing and macromolecule delivery.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Aug 21;6(8):2483-540. doi: 10.3390/toxins6082483. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25153255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-hemolysin nanopore allows discrimination of the microcystins variants.RSC Adv. 2019 May 10;9(26):14683-14691. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10384d. eCollection 2019 May 9. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35516306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olenina L.V., Kuzmina T.I., Sobolev B.N., Kuraeva T.E., Kolesanova E.F. Identification of glycosaminoglycan-binding sites within hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2∗. J. Viral Hepat. 2005;12:584–593. - PubMed
-
- Hurst R.E., Moldwin R.M., Mulholland S.G. Bladder defense molecules, urothelial differentiation, urinary biomarkers, and interstitial cystitis. Urology. 2007;69:S17–S23. - PubMed
-
- Sagrista M.L., Mora M., De Madariaga M.A. Surface modified liposomes by coating with charged hydrophilic molecules. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2000;5:19–33.
-
- Suppiramaniam V., Vaithianathan T., Manivannan K., Dhanasekaran M., Parameshwaran K. Modulatory effects of dextran sulfate and fucoidan on binding and channel properties of AMPA receptors isolated from rat brain. Synapse. 2006;60:456–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

