Variations of brain endothelial nitric oxide synthase concentration in rat and mouse cortex
- PMID: 19948238
- PMCID: PMC2818859
- DOI: 10.1016/j.niox.2009.11.006
Variations of brain endothelial nitric oxide synthase concentration in rat and mouse cortex
Abstract
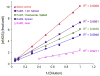
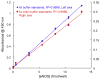
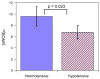
No information exists on the differences of eNOS concentration in brain tissue, [eNOS](br), between animals during normal and hypotensive blood pressure and both between and within animals during moderate hypotension. To address these questions, we modified a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit for determining murine [eNOS](br) since no method exists to measure [eNOS](br). Optimization of the kit ELISA procedure using brain cortex homogenates from 3 normotensive rats and 1 wild-type and 1 eNOS(-/-) (ko) mouse included recovery evaluation for each sample and the use of an "eNOS-free" homogenate calibrator diluent obtained from a mutant eNOS-ko mouse. Initial spike-and-recovery values of 12.5-27% suggesting a substantial sample matrix effect were improved with lipid removal treatment to 37.3% and to 70% with 1:20 dilution of the sample. Calibration standards prepared using eNOS-free buffer increased recovery values to 78% in micro-punch samples. The optimized ELISA was used in micro-punch (<1mg) brain cortex samples from 6 hypotensive rats. Whole brain [eNOS](br) varied considerably from 5-11fmol/mg wet weight and was different between normo- and hypotensive animals (p=0.023). The variability of [eNOS](br) due to moderate hypotension in micro-punch rat brain cortex samples was composed of both between (24%) and within (76%) animal components. The differences and variability of [eNOS](br) between normo- and hypotensive animals, and between and within hypotensive animals suggests the potential utility of its measurement for investigations of cerebrovascular physiology and that [eNOS](br) itself could be an important factor in cerebrovascular regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral microvascular dilation during hypotension and decreased oxygen tension: a role for nNOS.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):H2193-201. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00190.2007. Epub 2007 Jul 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17630350
-
Decreased arteriolar density in endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice is due to hypertension, not to the constitutive defect in endothelial nitric oxide synthase enzyme.J Hypertens. 2002 Feb;20(2):273-80. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200202000-00017. J Hypertens. 2002. PMID: 11821712
-
cGMP-mediated negative-feedback regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression by nitric oxide.Hypertension. 1999 Dec;34(6):1237-41. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.34.6.1237. Hypertension. 1999. PMID: 10601124
-
Investigation of vascular responses in endothelial nitric oxide synthase/cyclooxygenase-1 double-knockout mice: key role for endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in the regulation of blood pressure in vivo.Circulation. 2005 Feb 15;111(6):796-803. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000155238.70797.4E. Epub 2005 Feb 7. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15699263
-
Neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene knockout mice.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999 Nov;32(11):1353-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x1999001100005. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999. PMID: 10559836 Review.
Cited by
-
Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats.Foods. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):1256. doi: 10.3390/foods14071256. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang Z, Huang PL, Ma J, Meng W, Ayata C, Fishman MC, Moskowitz MA. Enlarged infarcts in endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice are attenuated by nitro-L-arginine. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:981–987. - PubMed
-
- Jones SC, Easley KA, Radinsky CR, Chyatte D, Furlan AJ, Perez-Trepichio AD. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition depresses the height of the cerebral blood flow-pressure autoregulation curve during moderate hypotension. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003;23:1085–1095. - PubMed
-
- Toyoda K, Fujii K, Ibayashi S, Nagao T, Kitazono T, Fujishima M. Role of nitric oxide in regulation of brain stem circulation during hypotension. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1089–1096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

