Targeted SERCA2a gene expression identifies molecular mechanism and therapeutic target for arrhythmogenic cardiac alternans
- PMID: 19948504
- PMCID: PMC2795134
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCEP.109.863118
Targeted SERCA2a gene expression identifies molecular mechanism and therapeutic target for arrhythmogenic cardiac alternans
Abstract
Background: Beat-to-beat alternans of cellular repolarization is closely linked to ventricular arrhythmias in humans. We hypothesized that sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium reuptake by SERCA2a plays a central role in the mechanism of cellular alternans and that increasing SERCA2a gene expression will retard the development of cellular alternans.
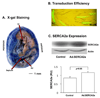
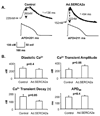
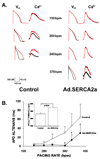
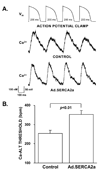
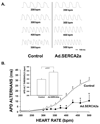
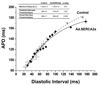
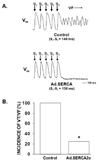
Methods and results: In vivo gene transfer of a recombinant adenoviral vector with the transgene for SERCA2a (Ad.SERCA2a) was performed in young guinea pigs. Isolated myocytes transduced with Ad.SERCA2a exhibited improved sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) reuptake (P<0.05) and were markedly resistant to cytosolic calcium alternans (P<0.05) under repetitive constant action potential clamp conditions (ie, when alternation of action potential duration was prevented), proving that sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) cycling is an important mechanism in the development of cellular alternans. Similarly, SERCA2a overexpression in the intact heart demonstrated significant resistance to alternation of action potential duration when compared with control hearts (heart rate threshold, 484+/-25 bpm versus 396+/-11 bpm, P<0.01), with no change in action potential duration restitution slope. Importantly, SERCA2a overexpression produced a 4-fold reduction in susceptibility to alternans-mediated ventricular arrhythmias (P<0.05).
Conclusions: These data provide new evidence that sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) reuptake directly modulates susceptibility to cellular alternans. Moreover, SERCA2a overexpression suppresses cellular alternans, interrupting an important pathway to cardiac fibrillation in the intact heart.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase 2a gene delivery to restore electrical stability in the failing heart.Circulation. 2012 Oct 23;126(17):2095-104. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.071480. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 23019291 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial SERCA2a Overexpression Has No Affect on Cardiac Alternans but Promotes Arrhythmogenic SR Ca2+ Triggers.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 9;10(9):e0137359. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137359. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26352986 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular correlates of repolarization alternans in cardiac myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005 Sep;39(3):419-28. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.06.004. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 16026799
-
The cardiac sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase: a potent target for cardiovascular diseases.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008 Sep;5(9):554-65. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1301. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008. PMID: 18665137 Review.
-
SERCA2a gene therapy in heart failure: an anti-arrhythmic positive inotrope.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;171(1):38-54. doi: 10.1111/bph.12472. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24138023 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Refractoriness of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release determines Ca2+ alternans in atrial myocytes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;302(11):H2310-20. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00079.2012. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22467301 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of gene therapy as a treatment for heart failure.J Clin Invest. 2013 Jan;123(1):53-61. doi: 10.1172/JCI62837. Epub 2013 Jan 2. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23281410 Free PMC article.
-
SERCA2a dysfunction in the pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a direct role is yet to be established.Heart Fail Rev. 2025 May;30(3):545-564. doi: 10.1007/s10741-025-10487-1. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 39843817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene therapy to treat cardiac arrhythmias.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Sep;12(9):531-46. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.61. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25917154 Review.
-
Impaired Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Uptake and Release Promote Electromechanically and Spatially Discordant Alternans: A Computational Study.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2016 Jun 23;10(Suppl 1):1-15. doi: 10.4137/CMC.S39709. eCollection 2016. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27385917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bers DM. Altered cardiac myocyte Ca regulation in heart failure. Physiology (Bethesda) 2006;21:380–387. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield DM, Steinman RC, Namerow PB, Parides M, Davidenko J, Kaufman ES, Shinn T, Curtis A, Fontaine J, Holmes D, Russo A, Tang C, Bigger JT., Jr Microvolt T-wave alternans distinguishes between patients likely and patients not likely to benefit from implanted cardiac defibrillator therapy: a solution to the Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial (MADIT) II conundrum. Circulation. 2004;110:1885–1889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

