A new isoquinolinium derivative, Cadein1, preferentially induces apoptosis in p53-defective cancer cells with functional mismatch repair via a p38-dependent pathway
- PMID: 19948725
- PMCID: PMC2823446
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070466
A new isoquinolinium derivative, Cadein1, preferentially induces apoptosis in p53-defective cancer cells with functional mismatch repair via a p38-dependent pathway
Abstract
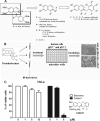
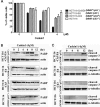
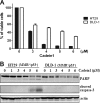
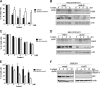
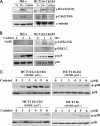
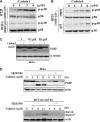
We screened a protoberberine backbone derivative library for compounds with anti-proliferative effects on p53-defective cancer cells. A compound identified from this small molecule library, cadein1 (cancer-selective death inducer 1), an isoquinolinium derivative, effectively leads to a G(2)/M delay and caspase-dependent apoptosis in various carcinoma cells with non- functional p53. The ability of cadein1 to induce apoptosis in p53-defective colon cancer cells was tightly linked to the presence of a functional DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, which is an important determinant in chemosensitivity. Cadein1 was very effective in MMR(+)/p53(-) cells, whereas it was not effective in p53(+) cells regardless of the MMR status. Consistently, when the function of MMR was blocked with short hairpin RNA in SW620 (MMR(+)/p53(-)) cells, cadein1 was no longer effective in inducing apoptosis. Besides, the inhibition of p53 increased the pro-apoptotic effect of cadein1 in HEK293 (MMR(+)/p53(+)) cells, whereas it did not affect the response to cadein1 in RKO (MMR(-)/p53(+)) cells. The apoptotic effects of cadein1 depended on the activation of p38 but not on the activation of Chk2 or other stress-activated kinases in p53-defective cells. Taken together, our results show that cadein1 may have a potential to be an anti-cancer chemotherapeutic agent that is preferentially effective on p53-mutant colon cancer cells with functional MMR.
Figures

References
-
- Fuster J. J., Sanz-González S. M., Moll U. M., Andrés V. (2007) Trends Mol. Med. 13, 192–199 - PubMed
-
- Gudkov A. (2003) Cancer Biol. Ther. 2, 444–445 - PubMed
-
- Wei C. L., Wu Q., Vega V. B., Chiu K. P., Ng P., Zhang T., Shahab A., Yong H. C., Fu Y., Weng Z., Liu J., Zhao X. D., Chew J. L., Lee Y. L., Kuznetsov V. A., Sung W. K., Miller L. D., Lim B., Liu E. T., Yu Q., Ng H. H., Ruan Y. (2006) Cell 124, 207–219 - PubMed
-
- El-Deiry W. S. (2003) Oncogene 22, 7486–7495 - PubMed
-
- Lowe S. W., Ruley H. E., Jacks T., Housman D.E. (1993) Cell 74, 957–967 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

