Anti-Convulsant Activity of Boerhaavia diffusa: Plausible Role of Calcium Channel Antagonism
- PMID: 19948752
- PMCID: PMC3135233
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nep192
Anti-Convulsant Activity of Boerhaavia diffusa: Plausible Role of Calcium Channel Antagonism
Abstract
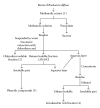
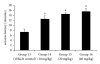
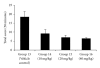
"Ethnopharmacological" use of roots of Boerhaavia diffusa (B. diffusa) in the treatment of epilepsy in Nigerian folk medicine and reports showing the presence of a calcium channel antagonistic compound "liriodendrin" in its roots, led us to undertake the present study. The study was designed to investigate the methanolic root extract of B. diffusa and its different fractions including liriodendrin-rich fraction for exploring the possible role of liriodendrin in its anti-convulsant activity. Air-dried roots of B. diffusa were extracted with methanol by cold maceration. The methanol soluble fraction of extract thus obtained was successively extracted to obtain liriodendrin-rich fraction and two side fractions, that is, chloroform fraction and phenolic compound fraction. Anti-convulsant activity of methanolic extract (1000, 1500 and 2000 mg kg(-1), intraperitoneally (i.p.)) and its different fractions, that is, liriodendrin-rich fraction (10, 20 and 40 mg kg(-1), i.p., chloroform fraction (20 mg kg(-1), i.p.) and phenolic compound fraction (1 mg kg(-1), i.p.) were studied in pentylenetetrazol (PTZ)-induced seizures (75 mg kg(-1), i.p.). The crude methanolic extract of B. diffusa and only its liriodendrin-rich fraction showed a dose-dependent protection against PTZ-induced convulsions. The liriodendrin-rich fraction also showed significant protection against seizures induced by BAY k-8644. These findings reiterated the anti-convulsant activity of methanolic extract of B. diffusa roots. Furthermore, it can be concluded that the observed anti-convulsant activity was due to its calcium channel antagonistic action as this activity was retained only in the liodendrin-rich fraction, which has additionally been confirmed by significant anti-convulsant activity of liriodendrin-rich fraction in BAY k-8644-induced seizures.
Figures

References
-
- Dhar ML, Dhar MM, Dhawan BN, Mehrotra BN, Ray C. Screening of Indian plants for biological activity: part I. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology. 1968;6:232–247. - PubMed
-
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. Indian Medicinal Plants. 2nd edition. III. Allahabad, India: Lalit Mohan Basu; 1956.
-
- Akah PA, Nwambie AI. Nigerian plants with anti-convulsant property. Fitoterapia. 1993;64(1):42–44.
-
- Gaitonde BB, Kulkarni HJ, Nabar SD. Diuretic activity of punarnava (Boerhaavia diffusa) Bull Haffkine Institute. 1974;2:p. 24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

