A structural analysis of the group II intron active site and implications for the spliceosome
- PMID: 19948765
- PMCID: PMC2802019
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1791310
A structural analysis of the group II intron active site and implications for the spliceosome
Abstract
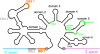
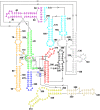
Group II introns are self-splicing, mobile genetic elements that have fundamentally influenced the organization of terrestrial genomes. These large ribozymes remain important for gene expression in almost all forms of bacteria and eukaryotes and they are believed to share a common ancestry with the eukaryotic spliceosome that is required for processing all nuclear pre-mRNAs. The three-dimensional structure of a group IIC intron was recently determined by X-ray crystallography, making it possible to visualize the active site and the elaborate network of tertiary interactions that stabilize the molecule. Here we describe the molecular features of the active site in detail and evaluate their correspondence with prior biochemical, genetic, and phylogenetic analyses on group II introns. In addition, we evaluate the structural significance of RNA motifs within the intron core, such as the major-groove triple helix and the domain 5 bulge. Having combined what is known about the group II intron core, we then compare it with known structural features of U6 snRNA in the eukaryotic spliceosome. This analysis leads to a set of predictions for the molecular structure of the spliceosomal active site.
Figures
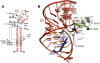
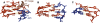
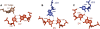
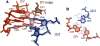
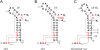
References
-
- Abramovitz DL, Friedman RA, Pyle AM. Catalytic role of 2′-hydroxyl groups within a group II intron active site. Science. 1996;271:1410–1413. - PubMed
-
- Blad H, Reiter NJ, Abildgaard F, Markley JL, Butcher SE. Dynamics and metal ion binding in the U6 RNA intramolecular stem–loop as analyzed by NMR. J Mol Biol. 2005;353:540–555. - PubMed
-
- Boeke JD. The unusual phylogenetic distribution of retrotransposons: A hypothesis. Genome Res. 2003;13:1975–1983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
