Experimental neonatal status epilepticus and the development of temporal lobe epilepsy with unilateral hippocampal sclerosis
- PMID: 19948825
- PMCID: PMC2797894
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090119
Experimental neonatal status epilepticus and the development of temporal lobe epilepsy with unilateral hippocampal sclerosis
Abstract
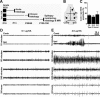
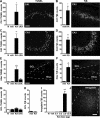
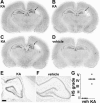
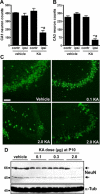
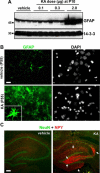
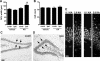
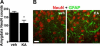
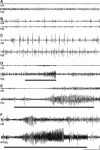
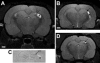
Hippocampal sclerosis is a common pathological finding in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy, including children, but a causal relationship to early-life seizures remains in question. Neonatal status epilepticus in animals can result in neuronal death within the hippocampus, although macroscopic features of hippocampal shrinkage are not evident at adulthood. Here, we examined electrophysiological and pathological consequences of focally evoked status epilepticus triggered by intra-amygdala microinjection of kainic acid in postnatal day 10 rat pups. Neonatal status epilepticus resulted in extensive neuronal death in the ipsilateral hippocampal CA1 and CA3 subfields and hilus, as assessed by DNA fragmentation and Fluoro-Jade B staining 72 hours later. The contralateral hippocampus was not significantly damaged. Histopathology at P55/P65 revealed unilateral hippocampal sclerosis (grade IV, modified Wyler/Watson scale) comprising >50% CA1 and CA3 neuron loss and astrogliosis. Additional features included hydrocephalus ex vacuo, modest dentate granule cell layer widening, and altered neuropeptide Y immunoreactivity indicative of synaptic rearrangement. Hippocampal atrophy was also evident on magnetic resonance imaging. Depth electrode recordings at adulthood detected spontaneous seizures that involved the ipsilateral hippocampus and amygdala. A significant positive correlation was found between hippocampal pathology grade and both frequency and duration of epileptic seizures at adulthood. The current study demonstrates that experimental neonatal status epilepticus can result in classical unilateral hippocampal sclerosis and temporal lobe epilepsy.
Figures
References
-
- Mathern GW, Babb TL, Armstrong DL. Hippocampal Sclerosis In Epilepsy: A Comprehensive Textbook. In: Engel JJ, Pedley TA, editors. Lippincott-Raven Publishers; Philadelphia: 1997. p. 133.
-
- Meldrum BS, Bruton CJ. Epilepsy. In: Adams JH, Duchen LW, editors. Oxford University Press; New York: 1992. p. 1246.
-
- Guerrini R. Epilepsy in children. Lancet. 2006;367:499–524. - PubMed
-
- Houser CR. Granule cell dispersion in the dentate gyrus of humans with temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 1990;535:195–204. - PubMed
-
- Davies KG, Hermann BP, Dohan FC, Jr, Foley KT, Bush AJ, Wyler AR. Relationship of hippocampal sclerosis to duration and age of onset of epilepsy, and childhood febrile seizures in temporal lobectomy patients. Epilepsy Res. 1996;24:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

