Cross-talk between vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases in the induction of neovascularization in vivo
- PMID: 19948826
- PMCID: PMC2797907
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.080642
Cross-talk between vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinases in the induction of neovascularization in vivo
Abstract
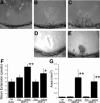
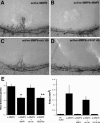
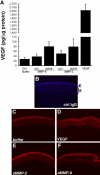
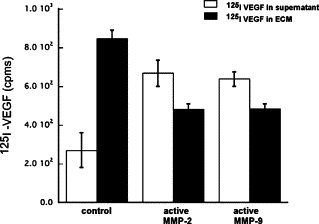
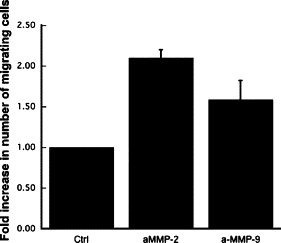
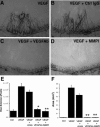
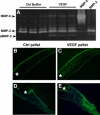
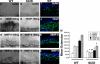
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a specialized group of enzymes capable of proteolytically degrading extracellular matrix proteins, have been postulated to play an important role in angiogenesis. It has been suggested that MMPs can regulate neovascularization using mechanisms other than simple remodeling of the capillary basement membrane. To determine the interplay between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and MMPs, we investigated the induction of angiogenesis by recombinant active MMPs and VEGF in vivo. Using a rat corneal micropocket in vivo angiogenesis assay, we observed that the active form of MMP-9 could induce neovascularization in vivo when compared with the pro- form of the enzyme as a control. This angiogenic response could be inhibited by neutralizing VEGF antibody, which suggests that MMPs acts upstream of VEGF. Additional in vitro studies using extracellular matrix loaded with radiolabeled VEGF determined that active MMPs can enzymatically release sequestered VEGF. Interestingly, in vivo angiogenesis induced by VEGF could be inhibited by MMP inhibitors, indicating that MMPs also act downstream of VEGF. In addition, inflammation plays an important role in the induction of angiogenesis mediated by both VEGF and MMPs. Our results suggest that MMPs act both upstream and downstream of VEGF and imply that potential combination therapies of VEGF and MMP inhibitors may be a useful therapeutic approach in diseases of pathological neovascularization.
Figures
References
-
- Pepper MS, Montesano R, Mandriota SJ, Orci L, Vassalli JD. Angiogenesis: a paradigm for balanced extracellular proteolysis during cell migration and morphogenesis. Enzyme Protein. 1996;49:138–162. - PubMed
-
- Matrisian LM. The matrix degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992;14:455–463. - PubMed
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21491–21494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

