Vitamin D receptor activators induce an anticalcific paracrine program in macrophages: requirement of osteopontin
- PMID: 19948844
- PMCID: PMC2809826
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.196576
Vitamin D receptor activators induce an anticalcific paracrine program in macrophages: requirement of osteopontin
Abstract
Objective: Vascular calcification is highly correlated with morbidity and mortality, and it is often associated with inflammation. Vitamin D may regulate vascular calcification and has been associated with cardiovascular survival benefits.
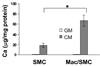
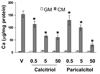
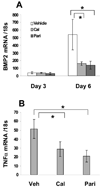
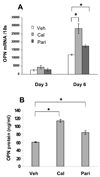
Methods and results: We developed a macrophage/smooth muscle cell (SMC) coculture system and examined the effects of vitamin D receptor activators (VDRA), calcitriol and paricalcitol, on SMC matrix calcification. We found that treatment of SMC alone with VDRA had little effect on phosphate-induced SMC calcification in vitro. However, coculture with macrophages promoted SMC calcification, and this was strikingly inhibited by VDRA treatment. Several VDRA-induced genes, including bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and osteopontin, were identified as candidate paracrine factors for the protective effect of VDRA. Of these, osteopontin was further investigated and found to contribute significantly to the inhibitory actions of VDRA on calcification in macrophage/SMC cocultures.
Conclusions: The ability of VDRA to direct a switch in the paracrine phenotype of macrophages from procalcific to anticalcific may contribute to their observed cardiovascular survival benefits.
Figures

References
-
- Rumberger JA, Simons DB, Fitzpatrick LA, Sheedy PF, Schwartz RS. Coronary artery calcium area by electron-beam computed tomography and coronary atherosclerotic plaque area. A histopathologic correlative study. Circulation. 1995;92:2157–2162. - PubMed
-
- Sangiorgi G, Rumberger JA, Severson A, Edwards WD, Gregoire J, Fitzpatrick LA, Schwartz RS. Arterial calcification and not lumen stenosis is highly correlated with atherosclerotic plaque burden in humans: a histologic study of 723 coronary artery segments using nondecalcifying methodology. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:126–133. - PubMed
-
- Loecker TH, Schwartz RS, Cotta CW, Hickman JR., Jr Fluoroscopic coronary artery calcification and associated coronary disease in asymptomatic young men. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;19:1167–1172. - PubMed
-
- Beadenkopf WG, Daoud AS, Love BM. Calcification in the coronary arteries and its relationship to arteriosclerosis and myocardial infarction. Am J Roentgenol. 1964;92:865–871. - PubMed
-
- Ehara S, Kobayashi Y, Yoshiyama M, Shimada K, Shimada Y, Fukuda D, Nakamura Y, Yamashita H, Yamagishi H, Takeuchi K, Naruko T, Haze K, Becker AE, Yoshikawa J, Ueda M. Spotty calcification typifies the culprit plaque in patients with acute myocardial infarction: an intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation. 2004;110:3424–3429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

