Histone H3K4 and K36 methylation, Chd1 and Rpd3S oppose the functions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Spt4-Spt5 in transcription
- PMID: 19948887
- PMCID: PMC2828714
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.111526
Histone H3K4 and K36 methylation, Chd1 and Rpd3S oppose the functions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Spt4-Spt5 in transcription
Abstract
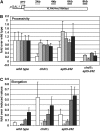
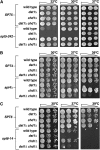
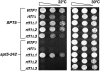
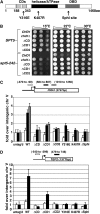
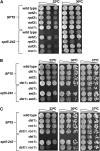
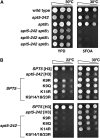
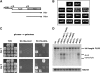
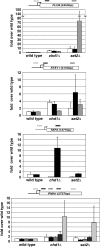
Spt4-Spt5, a general transcription elongation factor for RNA polymerase II, also has roles in chromatin regulation. However, the relationships between these functions are not clear. Previously, we isolated suppressors of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae spt5 mutation in genes encoding members of the Paf1 complex, which regulates several cotranscriptional histone modifications, and Chd1, a chromatin remodeling enzyme. Here, we show that this suppression of spt5 can result from loss of histone H3 lysines 4 or 36 methylation, or reduced recruitment of Chd1 or the Rpd3S complex. These spt5 suppressors also rescue the synthetic growth defects observed in spt5 mutants that also lack elongation factor TFIIS. Using a FLO8 reporter gene, we found that a chd1 mutation caused cryptic initiation of transcription. We further observed enhancement of cryptic initiation in chd1 isw1 mutants and increased histone acetylation in a chd1 mutant. We suggest that, as previously proposed for H3 lysine 36 methylation and the Rpd3S complex, H3 lysine 4 methylation and Chd1 function to maintain normal chromatin structures over transcribed genes, and that one function of Spt4-Spt5 is to help RNA polymerase II overcome the repressive effects of these histone modifications and chromatin regulators on transcription.
Figures

References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman et al., 1991. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York.
-
- Bannister, A. J., P. Zegerman, J. F. Partridge, E. A. Miska, J. O. Thomas et al., 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410 120–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

