Blockade of X4-tropic HIV-1 cellular entry by GSK812397, a potent noncompetitive CXCR4 receptor antagonist
- PMID: 19949058
- PMCID: PMC2812144
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01293-09
Blockade of X4-tropic HIV-1 cellular entry by GSK812397, a potent noncompetitive CXCR4 receptor antagonist
Abstract
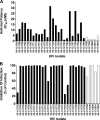
GSK812397 is a potent entry inhibitor of X4-tropic strains of HIV-1, as demonstrated in multiple in vitro cellular assays (e.g., in peripheral blood mononuclear cells [PBMCs] and a viral human osteosarcoma [HOS] assay, mean 50% inhibitory concentrations [IC50s]+/-standard errors of the means were 4.60+/-1.23 nM and 1.50+/-0.21 nM, respectively). The primary in vitro potency of GSK812397 was not significantly altered by the addition of serum proteins (2.55 [+/-0.12]-fold shift in the presence of human serum albumin and alpha-acid glycoprotein in the PBMC assay). Pharmacological characterization of GSK812397 in cell-based functional assays revealed it to be a noncompetitive antagonist of the CXCR4 receptor, with GSK812397 producing a concentration-dependent decrease in both an SDF-1-mediated chemotaxis and intracellular calcium release (IC50s were 0.34+/-0.01 nM and 2.41+/-0.50 nM, respectively). With respect to the antiviral activity of GSK812397, it was effective against a broad range of X4- and X4R5-utilizing clinical isolates. The potency and efficacy of GSK812397 were dependent on the individual isolate, with complete inhibition of infection observed with 24 of 30 isolates. GSK812397 did not show any detectable in vitro cytotoxicity and was highly selective for CXCR4, as determined using a wide range of receptors, enzymes, and transporters. Moreover, GSK812397 demonstrated acceptable pharmacokinetic properties and bioavailability across species. The data demonstrate that GSK812397 has antiviral activity against a broad range of X4-utilizing strains of HIV-1 via a noncompetitive antagonism of the CXCR4 receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Reference deleted.
-
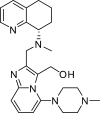
- Boggs, S., V. I. Elitzin, K. Gudmundsson, M. T. Martin, and M. J. Sharp. 2009. Kilogram-scale synthesis of the CXCR4 antagonist GSK812397. Org. Process Res. Dev. doi: 10.1021/op9000675. - DOI
-
- Buckley, C. D., N. Amft, P. F. Bradfield, D. Pilling, E. Ross, F. Arenzana-Seisdedos, A. Amara, S. J. Curnow, J. M. Lord, D. Scheel-Toellner, and M. Salmon. 2000. Persistent induction of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 by TGF-ß1 on synovial T cells contributes to their accumulation within the rheumatoid synovium. J. Immunol. 165:3423-3429. - PubMed
-
- Conklin, B. R., Z. Farfel, K. D. Lustig, D. Julius, and H. R. Bourne. 1993. Substitution of three amino acids switches receptor specificity of Gq alpha to that of Gi alpha. Nature 363:274-276. - PubMed
-
- Deng, H., D. Unutmaz, V. N. Kewalramani, and D. R. Littman. 1997. Expression cloning of new receptors used by simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature 388:296-300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

