Cardiac resynchronisation therapy and the role of optimal device utilisation
- PMID: 19949479
- PMCID: PMC2758352
- DOI: 10.1007/BF03086283
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy and the role of optimal device utilisation
Abstract
Despite established selection criteria, 30 to 40% of patients do not respond to cardiac resynchronisation therapy. By optimising programming of the device response to cardiac resynchronisation, therapy can be improved. (Neth Heart J 2009;17:354-7.).
Figures
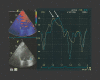
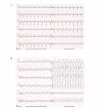

References
-
- Manolis AS. Cardiac resynchronization therapy in congestive heart failure: Ready for prime time? Heart Rhythm 2004;1:355–63. - PubMed
-
- Bristow MR, Saxon LA, Boehmer J, Krueger S, Kass DA, De Marco T, et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy with or without an implantable defibrillator in advanced chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2140–50. - PubMed
-
- Cleland JG, Daubert JC, Erdmann E, Freemantle N, Gras D, Kappenberger L, et al. The effect of cardiac resynchronization on morbidity and mortality in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1539–49. - PubMed
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, et al. ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur J Heart Fail 2008;10:933–89. - PubMed
-
- Ypenburg C, van Bommel RJ, Delgado V, Mollema SA, Bleeker GB, Boersma E, et al. Optimal left ventricular lead position predicts reverse remodeling and survival after cardiac resynchronization therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;52:1402–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
