Cardioprotective effects of alpha-lipoic Acid on myocardial reperfusion injury: suppression of reactive oxygen species generation and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 19949619
- PMCID: PMC2771824
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2009.39.9.359
Cardioprotective effects of alpha-lipoic Acid on myocardial reperfusion injury: suppression of reactive oxygen species generation and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
Background and objectives: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase play an important role in the development of myocardial reperfusion injury. In this study, we examined whether treatment with alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) before reperfusion could prevent myocardial reperfusion injury in vivo.
Materials and methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to a 45-minute left anterior descending coronary artery ligation followed by 45- or 10-minute reperfusion. ALA was administered 10 minutes prior to reperfusion. The infarct size ratio of the infarct area to the ischemic area at risk, was measured based on 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg of ALA, with propidium iodide (PI) fluorescence. Apoptosis was evaluated by TdT-mediated dUDP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. The generation of intracellular ROS was evaluated using the fluorogenic probe, dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (CM-H(2)DCFDA). Western blot analysis was performed for MAP kinase (pERK 1/2 and pJNK 1/2) activity.
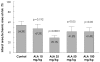
Results: The infarct size, according to ALA dose, was significantly suppressed 29.1% with ALA 25 mg/kg (p<0.0001), 41.5% with 50 mg/kg (p<0.05), and 41.4% with 100 mg/kg (p<0.05) compared to the controls (54.3%). However, the results were not significantly different with 47.2% of the ALA 10 mg/kg (p=0.192). A few apoptotic nucleoli were detected in the ALA 25 mg/kg group, but were frequently detected in the control group. The ROS generation was significantly suppressed (p<0.0001), the activity of pERK 1/2 was significantly increased (p<0.05) and the activity of pJNK 1/2 was significantly decreased (p<0.05) in the ALA 25 mg/kg group compared to the controls.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggested that adequate doses of ALA before reperfusion was effective for the prevention of myocardial reperfusion injury in vivo. This cardioprotective activity of ALA might be associated with an anti-apoptotic effect of ALA via suppression of ROS generation, increase of pERK 1/2 and decrease of pJNK 1/2 activity.
Keywords: Alpha-lipoic acid; Apoptosis; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Myocardial reperfusion injury; Reactive oxygen species.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Luteolin inhibits ROS-activated MAPK pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Life Sci. 2015 Feb 1;122:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2014.11.014. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25476833
-
Pharmacological postconditioning with Neuregulin-1 mimics the cardioprotective effects of ischaemic postconditioning via ErbB4-dependent activation of reperfusion injury salvage kinase pathway.Mol Med. 2018 Jul 31;24(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0040-7. Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30134819 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant human-activated protein C inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.Coron Artery Dis. 2007 Feb;18(1):61-6. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e328010a44a. Coron Artery Dis. 2007. PMID: 17172932
-
Limb remote postconditioning alleviates cerebral reperfusion injury through reactive oxygen species-mediated inhibition of delta protein kinase C in rats.Anesth Analg. 2011 Nov;113(5):1180-7. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31822b885f. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21865497
-
Simvastatin relieves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through hedgehog signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jun;24(11):6400-6408. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21538. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32572937
Cited by
-
Metformin and alpha lipoic acid ameliorate hypothyroidism and its complications in adult male rats.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jun 8;21(2):1327-1337. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01063-7. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36404819 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Efficacy of Alpha-Lipoic Acid against Acute Myocardial Infarction and Chronic Left Ventricular Remodeling in Mice.Cardiol Res Pract. 2020 Jan 7;2020:6759808. doi: 10.1155/2020/6759808. eCollection 2020. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32411448 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin modulates SERCA2a via Sp1 upregulation to attenuate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 21;10(1):15407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72325-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32958799 Free PMC article.
-
α-Lipoic acid reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58371. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058371. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eefting F, Rensing B, Wigman J, et al. Role of apoptosis in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61:414–426. - PubMed
-
- Zhao ZQ, Nakamura M, Wang NP, et al. Reperfusion induces myocardial apoptotic cell death. Cardiovasc Res. 2000;45:651–660. - PubMed
-
- Anversa P, Cheng W, Liu Y, Leri A, Redaelli G, Kajstura J. Apoptosis and myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 1998;93(Suppl 3):8–12. - PubMed
-
- Zweier JL. Measurement of superoxide-derived free radicals in the reperfused heart: evidence for a free radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:1353–1357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

