Long-term effectiveness and tolerability of topiramate in children with epilepsy under the age of 2 years: 4-year follow-up
- PMID: 19949663
- PMCID: PMC2775855
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1078
Long-term effectiveness and tolerability of topiramate in children with epilepsy under the age of 2 years: 4-year follow-up
Abstract
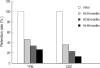
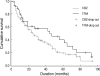
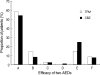
This is a long-term, open label, observational study aimed to broaden our clinical experiences in managing infants and toddlers with epilepsy. The long-term retention rate and side effects of topiramate (TPM) in them were evaluated and compared with carbamazepine (CBZ). A total of 146 children were involved in the study (TPM=41, CBZ=105). The retention rates at 24 , 36, and 48 months were 46.3%, 34.1%, 26.8% for TPM and 36.2%, 23.8%, 13.3% for CBZ, respectively. At 6 months after starting antiepileptic drugs (AED), the seizure freedom or clinical efficacy (seizure reduction rate more than 50 percent) were 73.2% for TPM and 62.9% for CBZ. The major side effects led to discontinuation included psychomotor slowing, poor oral intake from TPM and sleepiness and skin rash from CBZ. TPM was discontinued due to side effects in one case (2.4%) and lack of efficacy in five cases (12.2%), whereas CBZ was discontinued due to lack of efficacy (22.9%) and side effects (6.7%). As compared with CBZ, TPM showed the same long-term retention rate in children under the age of 2 yr, and no serious side effects. It is therefore concluded that TPM can be considered as a major AED for treating children with epilepsy under the age of 2 yr.
Keywords: Adverse Effects; Carbamazepine; Topiramate; Treatment Outcome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Efficacy of carbamazepine, valproate and topiramate in the treatment of medial temporal epilepsy in children].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010;110(4):41-7. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010. PMID: 20517209 Russian.
-
[Comparative efficacy of carbamazepine, valproic acid and topiramate in symptomatic and cryptogenic frontal lobe epilepsy in children].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010;110(6):58-65. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010. PMID: 20559276 Russian.
-
[Comparative efficacy of carbamazepine, valproic acid and topiramate in symptomatic and cryptogenic occipital lobe epilepsy in children].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010;110(5 Suppl 1):39-44. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2010. PMID: 20559266 Clinical Trial. Russian.
-
Drug interaction profile of topiramate.Epilepsia. 1996;37 Suppl 2:S14-S17. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1996.tb06028.x. Epilepsia. 1996. PMID: 8641241 Review.
-
Topiramate monotherapy in the treatment of newly or recently diagnosed epilepsy.Clin Ther. 2008 Jul;30(7):1180-95. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(08)80045-8. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18691980 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends in Antiepileptic Drug Prescriptions for Childhood Epilepsy at a Tertiary Children's Hospital in Korea, 2001-2012.Paediatr Drugs. 2015 Dec;17(6):487-96. doi: 10.1007/s40272-015-0147-z. Paediatr Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26400586
-
Topiramate for the treatment of neonatal seizures.Pediatr Neurol. 2011 Jun;44(6):439-42. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2011.01.006. Pediatr Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21555055 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic and Dietary Treatments for Epilepsies in Children Aged 1-36 Months: A Systematic Review.Neurology. 2023 Jan 3;100(1):e16-e27. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000201026. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Neurology. 2023. PMID: 36270899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aicardi J. Risks and benefits of new antiepileptic agents in children. Rev Neurol. 2000;31:376–381. - PubMed
-
- Bourgeois BF. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of topiramate. J Child Neurol. 2000;15(Suppl 1):S27–S30. - PubMed
-
- Bebin M. Pediatric partial and generalized seizures. J Child Neurol. 2002;17(Suppl 1):S65–S69. - PubMed
-
- Blumkin L, Lerman-Sagie T, Houri T, Gilad E, Nissenkorn A, Ginsberg M, Watemberg N. Pediatric refractory partial status epilepticus responsive to topiramate. J Child Neurol. 2005;20:239–241. - PubMed
-
- Bootsma HP, Aldenkamp AP, Diepman L, Hulsman J, Lambrechts D, Leenen L, Majoie M, Schellekens A, de Krom M. The effect of antiepileptic drugs on cognition: patient perceived cognitive problems of topiramate versus levetiracetam in clinical practice. Epilepsia. 2006;47(Suppl 2):24–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

