Long-term results of laparoscopic Burch colposuspension for stress urinary incontinence in women
- PMID: 19949679
- PMCID: PMC2775871
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.6.1182
Long-term results of laparoscopic Burch colposuspension for stress urinary incontinence in women
Abstract
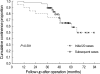
We evaluated the long-term efficacy of laparoscopic Burch colposuspension for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in women. A total of 68 patients who underwent extraperitoneal laparoscopic Burch colposuspensions with more than a 3-yr follow-up were included. The colposuspension was performed by using two non-absorbable sutures on each side. The patients were considered to be cured of SUI if they had a negative result of cough stress test and there were no reports of urine leakage during physical stress. The mean follow-up period was 52 months (range, 36 to 83 months). The overall subjective cure rate was reported in 49 patients (72%). There was no significant difference between the cured and non-cured group in terms of clinical parameters. The cure rate tended to decline gradually over time and it was more deteriorated significantly after 4 yr of surgery. Based on these results, we recommend that long-term follow-up is needed when evaluating the clinical efficacy of anti-incontinence surgery.
Keywords: Follow-Up Studies; Laparoscopy; Urinary Incontinence, Stress.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, van Kerrebroeck P, Victor A, Wein A. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21:167–178. - PubMed
-
- McDougall EM. Laparoscopic management of female urinary incontinence. Urol Clin North Am. 2001;28:145–149. - PubMed
-
- Burch JC. Urethrovaginal fixation to Cooper's ligament for correction of stress incontinence, cystocele, and prolapse. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961;81:281–290. - PubMed
-
- Alcalay M, Monga A, Stanton SL. Burch colposuspension: a 10-20 year follow up. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995;102:740–745. - PubMed
-
- Drouin J, Tessier J, Bertrand PE, Schick E. Burch colposuspension: long-term results and review of published reports. Urology. 1999;54:808–814. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical