Factors for determining survival in acute organophosphate poisoning
- PMID: 19949736
- PMCID: PMC2784981
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.4.362
Factors for determining survival in acute organophosphate poisoning
Abstract
Background/aims: Organophosphate poisoning has a high mortality rate. Recently, differences among organophosphorus insecticides in human self-poisoning were reported. This study investigated the prognostic risk factors and the mortality of different organophosphates following acute organophosphate poisoning.
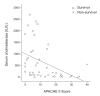
Methods: This retrospective study included 68 patients with acute organophosphate poisoning. We investigated patient survival according to initial parameters, including the initial Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score, serum cholinesterase level, and hemoperfusion and evaluated the mortality according to organophosphate types.
Results: Thirteen of the 68 patients died. The agents responsible for mortality were different. The APACHE II score was a significant predictor of mortality (odds ratio [OR], 1.194; p<0.01; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.089 to 1.309) and respiratory failure (OR, 1.273; p<0.01; 95% CI, 1.122 to 1.444). The mortality was 0% for dichlorvos, malathion, chlorpyrifos and profenofos. However, other organophosphates showed different mortality (16.7% for O-ethyl-O-4-nitrophenyl phenylphosphonothioate, 25% for phenthoate, 37.5% for phosphamidon, 50% for methidathion). The usefulness of hemoperfusion appears to be limited.
Conclusions: The initial APACHE II score is a useful prognostic indicator, and different organophosphates have different mortality.
Keywords: APACHE; Organophosphate; Survival.
Figures

References
-
- Goldfrank LR. Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies. 7th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; 2002. pp. 1346–1360.
-
- Bardin PG, van Eeden SF, Joubert JR. Intensive care management of acute organophosphate poisoning: a 7-year experience in the western Cape. S Afr Med J. 1987;72:593–597. - PubMed
-
- Munidasa UA, Gawarammana IB, Kularatne SA, Kumarasiri PV, Goonasekera CD. Survival pattern in patients with acute organophosphate poisoning receiving intensive care. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2004;42:343–347. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2000-2001. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001. WHO/PCS/01.4.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
