School, family, and peer factors and their association with substance use in Hispanic adolescents
- PMID: 19949868
- PMCID: PMC2916637
- DOI: 10.1007/s10935-009-0197-5
School, family, and peer factors and their association with substance use in Hispanic adolescents
Abstract
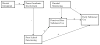
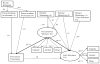
The purpose of the present study was to examine how relationships among family, school, and peer factors relate to likelihood of substance use in Hispanic adolescents. Results indicated that only perceived peer substance use was directly related to adolescents' own substance use. A significant interaction was found between parental monitoring and peer use vis-à-vis substance use, which suggests that the relationship between parental monitoring and the adolescents' own use was significantly stronger among youth who reported that more of their friends used substances. Implications of these results for the design of substance use preventive interventions are discussed. Editors' Strategic Implications: This research is promising both in terms of the implications for targets of prevention programming and for the application of ecodevelopmental theory, which might guide similar efforts with different cultural groups.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An empirical test of ecodevelopmental theory in predicting HIV risk behaviors among Hispanic youth.Health Educ Behav. 2010 Feb;37(1):97-114. doi: 10.1177/1090198109349218. Health Educ Behav. 2010. PMID: 20130302 Free PMC article.
-
Ecodevelopmental predictors of early initiation of alcohol, tobacco, and drug use among Hispanic adolescents.J Sch Psychol. 2015 Jun;53(3):195-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jsp.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Sch Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26054814 Free PMC article.
-
Acculturation, social self-control, and substance use among Hispanic adolescents.Psychol Addict Behav. 2013 Sep;27(3):674-86. doi: 10.1037/a0032836. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Psychol Addict Behav. 2013. PMID: 23772765 Free PMC article.
-
Ecodevelopmental x intrapersonal risk: substance use and sexual behavior in Hispanic adolescents.Health Educ Behav. 2009 Feb;36(1):45-61. doi: 10.1177/1090198107311278. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Health Educ Behav. 2009. PMID: 18326053 Free PMC article.
-
Moderators of the association between peer and target adolescent substance use.Addict Behav. 2014 Jan;39(1):48-70. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.09.025. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24183303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Family and parenting characteristics associated with marijuana use by Chilean adolescents.Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011 Mar;2011(2):1-11. doi: 10.2147/SAR.S16432. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2011. PMID: 21660209 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic Frontolimbic Connectivity and Mood Symptoms in Young Adult Cannabis Users.Front Public Health. 2019 Nov 1;7:311. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00311. eCollection 2019. Front Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31737591 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating Change in Drinking Cognitions and Behaviors Among Three Immigrant Generations of Latinx Youth Through a School-Based Intervention: Findings From a Multi-Site Clinical Trial.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Nov 16;11:574487. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.574487. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33304281 Free PMC article.
-
Profile and predictors of adolescent tobacco use in Ghana: evidence from the 2017 Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS).J Prev Med Hyg. 2021 Sep 15;62(3):E664-E672. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.3.2035. eCollection 2021 Sep. J Prev Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 34909494 Free PMC article.
-
Sociocultural determinants of substance misuse among adult Latinas of Caribbean and South and Central American descent: A longitudinal study of a community-based sample.J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2018 Jul-Sep;17(3):303-323. doi: 10.1080/15332640.2016.1201716. Epub 2016 Jul 19. J Ethn Subst Abuse. 2018. PMID: 27436513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Dumenci L, Rescorla LA. Samples of youth: Self, parent, and teacher reports. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders. 2002;10(4):194–203.
-
- Bank B. Some paradoxes of gender equity and schooling. In: Bank B, Hall P, editors. Gender equity and schooling. New York: Garland; 1997. pp. 3–30.
-
- Benjet C, Borges G, Medina-Mora ME, Fleiz C, Blanco J, Zambrano J, et al. Prevalence and socio-demographic correlates of drug use among adolescents: Results from the Mexican adolescent mental health survey. Addiction. 2007;102(8):1261–1268. - PubMed
-
- Bentler PM, Satorra A. Hierarchical regression without phantom factors. Structural Equation Modeling. 2000;7(2):287–291.
-
- Bernstein R. Minority population tops 100 million. 2007. Retrieved May 17, 2007, from http://www.census.gov/dcmd/www/embargo/popest/national/pio-nat_stat.html.

