Adenosine mediated desensitization of cAMP signaling enhances T-cell responses
- PMID: 19950175
- PMCID: PMC3468332
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200939586
Adenosine mediated desensitization of cAMP signaling enhances T-cell responses
Abstract
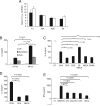
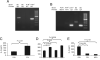
Adenosine has long been regarded as a crucial anti-inflammatory agent that protects the host from excessive damage. It has been reported to play an important role in suppressing immune activation, particularly that of T cells. However, it is a general observation that induction of T-cell activation is an efficient event despite the high adenosine levels that are often present in the affected host due to injury or stress. We report here that prior to antigenic stimulation via TCR/CD3, exposure of T cells to adenosine desensitizes adenosine receptors, so as to create a window of time where the T cells are insensitive to this ubiquitous suppressor. T cells from mice that were pre-exposed to this manipulation showed stronger responses to antigenic stimulation; therefore, the P1 adenosine receptor desensitization demonstrated an adjuvant-like effect. Our results suggest that adenosine receptor desensitization may be a mechanism for T cells to escape the general suppression during early points of T-cell activation and may emerge as a potential alternative for vaccine adjuvants.
Figures

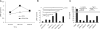
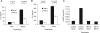
Similar articles
-
The role of mechanical forces and adenosine in the regulation of intestinal enterochromaffin cell serotonin secretion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):G397-405. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00087.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22038827 Free PMC article.
-
A2A adenosine receptor induction inhibits IFN-gamma production in murine CD4+ T cells.J Immunol. 2005 Jan 15;174(2):1073-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.2.1073. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15634932
-
Pharmacological preconditioning with adenosine A(1) receptor agonist suppresses cellular immune response by an A(2A) receptor dependent mechanism.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 May;20(1):205-12. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24560904
-
Role of A2a extracellular adenosine receptor-mediated signaling in adenosine-mediated inhibition of T-cell activation and expansion.Blood. 1997 Aug 15;90(4):1600-10. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9269779
-
A1 and A2A adenosine receptor modulation of alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated contractility in human cultured prostatic stromal cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;141(2):302-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705535. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14751869 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Purinergic signalling and immune cells.Purinergic Signal. 2014 Dec;10(4):529-64. doi: 10.1007/s11302-014-9427-2. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Purinergic Signal. 2014. PMID: 25352330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Adenosine in Cancer Immunotherapy to Enhance T-Cell Function.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 6;10:925. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00925. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31244820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine-mediated immunosuppression in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.HNO. 2016 May;64(5):303-9. doi: 10.1007/s00106-016-0137-7. HNO. 2016. PMID: 27052632 Review. English.
References
-
- Hasko G, Cronstein BN. Adenosine: an endogenous regulator of innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:33–39. - PubMed
-
- Hershfield MS. New insights into adenosine-receptor-mediated immunosuppression and the role of adenosine in causing the immunodeficiency associated with adenosine deaminase deficiency. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005;35:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Yaar R, Jones MR, Chen JF, Ravid K. Animal models for the study of adenosine receptor function. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005;202:9–20. - PubMed
-
- Ohta A, Sitkovsky M. Role of G-protein-coupled adenosine receptors in downregulation of inflammation and protection from tissue damage. Nature. 2001;414:916–920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

