The role of sex hormones in the development of Th2 immunity in a gender-biased model of Trichuris muris infection
- PMID: 19950176
- PMCID: PMC3549561
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200939589
The role of sex hormones in the development of Th2 immunity in a gender-biased model of Trichuris muris infection
Abstract
Trichuris muris infection is an ideal model for defining T-cell-driven immunity, and also provides essential insights that may impact on potential helminth therapies currently in development. Conflicting host variables determine the efficiency of such treatments and we have identified host-derived sex steroid hormones as key factors in the development of immunity. The female-associated hormone 17-beta estradiol (E2) significantly enhanced the generation of a Th2 response in vitro; however, this stimulatory effect was found to be dispensable for the generation of immunity to Trichuris in the gender-biased IL-4KO mouse model. In contrast, the male-associated hormone dihydrotestosterone significantly inhibited the T-cell stimulatory capacity of DC and directly suppressed the immune response of male IL-4KO mice, with worm expulsion restored following castration. This finding was associated with dramatically reduced IL-18 mRNA expression suggesting androgens may act via this cytokine to suppress Th2 immunity to Trichuris. This study has critical implications for the development and efficacy of potential helminth therapeutics and identifies host gender - specifically sex hormones - as important factors in the development of Th2 immunity in susceptible and immunocompromised mice.
Figures

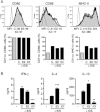

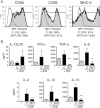

Comment in
-
Androgenetic alopecia may be associated with weaker COVID-19 T-cell immune response: An insight into a potential COVID-19 vaccine booster.Med Hypotheses. 2021 Jan;146:110439. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110439. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Med Hypotheses. 2021. PMID: 33308937 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Grencis RK, Bancroft AJ. Interleukin-13 – a key mediator in resistance to gastrointestinal-dwelling nematode parasites. Clin. Rev. Aller. Immunol. 2004;26:51–60. - PubMed
-
- Cliffe LJ, Humphreys NE, Lane TE, Potten CS, Booth C, Grencis RK. Accelerated intestinal epithelial cell turnover: a new mechanism of parasite expulsion. Science. 2005;308:1463–1465. - PubMed
-
- McDermott JR, Humphreys NE, Forman SP, Donaldson DD, Grencis RK. Intraepithelial NK cell-derived IL-13 induces intestinal pathology associated with nematode infection. J. Immunol. 2005;175:3207–3213. - PubMed
-
- Summers RW, Elliott DE, Urban JF, Jr, Thompson RA, Weinstock JV. Trichuris suis therapy for active ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:825–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

