Type I interferons are not critical for skin allograft rejection or the generation of donor-specific CD8+ memory T cells
- PMID: 19951284
- PMCID: PMC2806930
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02871.x
Type I interferons are not critical for skin allograft rejection or the generation of donor-specific CD8+ memory T cells
Abstract
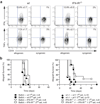
Type I interferons (IFN-I) link innate to adaptive immunity in microbial infection, autoimmune disease and tumor immunity. It is not known whether IFN-I have an equally central role in alloimmunity. Here we tested this possibility by studying skin allograft survival and donor-specific CD8+ T-cell responses in mice that lack the IFN-I receptor (IFN-IR-/-). We found that IFN-IR-/- mice reject fully allogeneic wild-type skin grafts at the same rate as wild-type recipients. Similarly, allograft rejection was not delayed if IFN-IR-/- male skin was transplanted to syngeneic IFN-IR-/- female mice. Quantitation of the male (H-Y)-specific CD8+ T-cell response in these mice revealed normal generation of donor-specific CD8+ effector T cells but fourfold reduction in CD8+ memory T cells. Memory CD8+ T cells generated in the absence of IFN-IR had normal phenotype and recall function, assessed by ex vivo cytokine production and the ability of IFN-IR-/- mice to mount second set rejection. Finally, these memory T cells were maintained at a constant number despite their inability to respond to IFN-1. Our findings indicate that IFN-I cytokines are not critical for acute allograft rejection or for the expansion and differentiation of donor-specific CD8+ T cells into long-lived, functional memory T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–336. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Sastre A, Biron CA. Type 1 interferons and the virus-host relationship: a lesson in detente. Science. 2006;312(5775):879–882. - PubMed
-
- Muller U, Steinhoff U, Reis LF, Hemmi S, Pavlovic J, Zinkernagel RM, et al. Functional role of type 1 and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994;(264) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

