Apolipoprotein E4 and sex affect neurobehavioral performance in primary school children
- PMID: 19952867
- PMCID: PMC2853744
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181cb8e68
Apolipoprotein E4 and sex affect neurobehavioral performance in primary school children
Abstract
Apolipoprotein E4 (apoE4) and female sex are risk factors for developing Alzheimer's disease. It is unclear whether apoE4 contributes to behavioral function at younger ages. Standard neuropsychological assessments [intelligence quotient (IQ), attention, and executive function] and a test developed in this laboratory (Memory Island test of spatial learning and memory) were used to determine whether E4 and sex affect neuropsychological performance in healthy primary school children (age 7-10). A medical history was also obtained from the mother to determine whether negative birth outcomes were associated with apoE4. Mothers of apoE4+ children were more likely to report that their newborn was placed in an intensive care unit. A sex difference in birth weight was noted among apoE4- (males > females), but not apoE4+, offspring. Conversely, among apoE4+, but not apoE4- children, there was a sex difference in the Wechsler Abbreviated Scale of Intelligence (WASI) vocabulary score favoring boys. ApoE4- girls had better visual recall than apoE4+ girls or apoE4- boys on the Family Pictures test. Finally, apoE4+, unlike apoE4-, children did not show spatial memory retention during the Memory Island probe trial. Thus, apoE4 may affect neurobehavioral performance, particularly spatial memory, and antenatal health decades before any clinical expression of neurodegenerative processes.
Figures


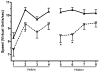
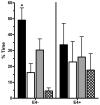
 : right, or
: right, or  : opposite quadrant (for additional details, see text).
: opposite quadrant (for additional details, see text).References
-
- Herz J, Beffert U. Apolipoprotein E receptor: Linking brain development and Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:51–58. - PubMed
-
- Mahley RW, Weisgraber KH, Innerarity TL, Rall SC., Jr Genetic defects in lipoprotein metabolism. Elevation of artherogenic lipoproteins caused by impaired catabolism. JAMA. 1991;265:78–83. - PubMed
-
- Shao Y, Gearing M, Mirra SS. Astrocyte-apolipoprotein E associations in senile plaques in Alzheimer disease and vascular lesions: a regional immunohistochemical study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:376–381. - PubMed

