Rapid and sustained nuclear-cytoplasmic ERK oscillations induced by epidermal growth factor
- PMID: 19953086
- PMCID: PMC2824491
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2009.90
Rapid and sustained nuclear-cytoplasmic ERK oscillations induced by epidermal growth factor
Abstract
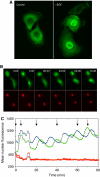
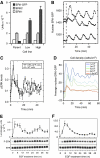
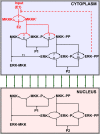
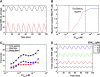
Although the ERK pathway has a central role in the response of cells to growth factors, its regulatory structure and dynamics are incompletely understood. To investigate ERK activation in real time, we expressed an ERK-GFP fusion protein in human mammary epithelial cells. On EGF stimulation, we observed sustained oscillations of the ERK-GFP fusion protein between the nucleus and cytoplasm with a periodicity of approximately 15 min. The oscillations were persistent (>45 cycles), independent of cell cycle phase, and were highly dependent on cell density, essentially disappearing at confluency. Oscillations occurred even at ligand doses that elicited very low levels of ERK phosphorylation, and could be detected biochemically in both transfected and nontransfected cells. Mathematical modeling revealed that negative feedback from phosphorylated ERK to the cascade input was necessary to match the robustness of the oscillation characteristics observed over a broad range of ligand concentrations. Our characterization of single-cell ERK dynamics provides a quantitative foundation for understanding the regulatory structure of this signaling cascade.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bhalla US, Ram PT, Iyengar R (2002) MAP kinase phosphatase as a locus of flexibility in a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling network. Science 297: 1018–1023 - PubMed
-
- Brightman FA, Fell DA (2000) Differential feedback regulation of the MAPK cascade underlies the quantitative differences in EGF and NGF signalling in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett 482: 169–174 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

