Comparison of substrate specificity of the ubiquitin ligases Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 using proteome arrays
- PMID: 19953087
- PMCID: PMC2824488
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2009.85
Comparison of substrate specificity of the ubiquitin ligases Nedd4 and Nedd4-2 using proteome arrays
Abstract
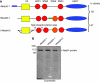
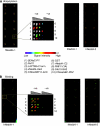
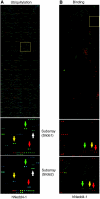
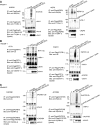
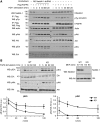
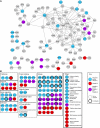
Target recognition by the ubiquitin system is mediated by E3 ubiquitin ligases. Nedd4 family members are E3 ligases comprised of a C2 domain, 2-4 WW domains that bind PY motifs (L/PPxY) and a ubiquitin ligase HECT domain. The nine Nedd4 family proteins in mammals include two close relatives: Nedd4 (Nedd4-1) and Nedd4L (Nedd4-2), but their global substrate recognition or differences in substrate specificity are unknown. We performed in vitro ubiquitylation and binding assays of human Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2, and rat-Nedd4-1, using protein microarrays spotted with approximately 8200 human proteins. Top hits (substrates) for the ubiquitylation and binding assays mostly contain PY motifs. Although several substrates were recognized by both Nedd4-1 and Nedd4-2, others were specific to only one, with several Tyr kinases preferred by Nedd4-1 and some ion channels by Nedd4-2; this was subsequently validated in vivo. Accordingly, Nedd4-1 knockdown or knockout in cells led to sustained signalling via some of its substrate Tyr kinases (e.g. FGFR), suggesting Nedd4-1 suppresses their signalling. These results demonstrate the feasibility of identifying substrates and deciphering substrate specificity of mammalian E3 ligases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
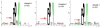

References
-
- Abriel H, Kamynina E, Horisberger JD, Staub O (2000) Regulation of the cardiac voltage-gated Na+ channel (H1) by the ubiquitin-protein ligase Nedd4. FEBS Lett 466: 377–380 - PubMed
-
- Abriel H, Staub O (2005) Ubiquitylation of ion channels. Physiology (Bethesda) 20: 398–407 - PubMed
-
- Anindya R, Aygun O, Svejstrup JQ (2007) Damage-induced ubiquitylation of human RNA polymerase II by the ubiquitin ligase Nedd4, but not Cockayne syndrome proteins or BRCA1. Mol Cell 28: 386–397 - PubMed
-
- Attisano L, Wrana JL (2002) Signal transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science 296: 1646–1647 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

