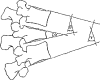
Inter- and intraobserver reliability of the vertebral, local and segmental kyphosis in 120 traumatic lumbar and thoracic burst fractures: evaluation in lateral X-rays and sagittal computed tomographies
- PMID: 19953277
- PMCID: PMC2899829
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-009-1231-2
Inter- and intraobserver reliability of the vertebral, local and segmental kyphosis in 120 traumatic lumbar and thoracic burst fractures: evaluation in lateral X-rays and sagittal computed tomographies
Abstract
Evaluation of the kyphosis angle in thoracic and lumbar burst fractures is often used to indicate surgical procedures. The kyphosis angle could be measured as vertebral, segmental and local kyphosis according to the method of Cobb. The vertebral, segmental and local kyphosis according to the method of Cobb were measured at 120 lateral X-rays and sagittal computed tomographies of 60 thoracic and 60 lumbar burst fractures by 3 independent observers on 2 separate occasions. Osteoporotic fractures were excluded. The intra- and interobserver reliability of these angles in X-ray and computed tomogram, using the intra class correlation coefficient (ICC) were evaluated. Highest reproducibility showed the segmental kyphosis followed by the vertebral kyphosis. For thoracic fractures segmental kyphosis shows in X-ray "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities (ICC 0.826, 0.802) and for lumbar fractures "good" to "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities (ICC = 0.790, 0.803). In computed tomography, the segmental kyphosis showed "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities (ICC = 0.824, 0.801) for thoracic and "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities (ICC = 0.874, 0.835) for the lumbar fractures. Regarding both diagnostic work ups (X-ray and computed tomography), significant differences were evaluated in interobserver reliabilities for vertebral kyphosis measured in lumbar fracture X-rays (p = 0.035) and interobserver reliabilities for local kyphosis, measured in thoracic fracture X-rays (p = 0.010). Regarding both fracture localizations (thoracic and lumbar fractures), significant differences could only be evaluated in interobserver reliabilities for the local kyphosis measured in computed tomographies (p = 0.045) and in intraobserver reliabilities for the vertebral kyphosis measured in X-rays (p = 0.024). "Good" to "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities for vertebral, segmental and local kyphosis in X-ray make these angles to a helpful tool, indicating surgical procedures. For the practical use in lateral X-ray, we emphasize the determination of the segmental kyphosis, because of the highest reproducibility of this angle. "Good" to "excellent" inter- and intraobserver reliabilities for these three angles could also be evaluated in computed tomographies. Therefore, also in computed tomography, the use of these three angles seems to be generally possible. For a direct correlation of the results in lateral X-ray and in computed tomography, further studies should be needed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Traumatic thoracic spine fractures: inter- and intraobserver reliability of vertebral, local and segmental kyphosis in lateral X-rays].Z Orthop Unfall. 2009 Jul-Aug;147(4):481-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1185712. Z Orthop Unfall. 2009. PMID: 19771675 German.
-
Inter- and intra-observer reliability of the Cobb angle in the measurement of vertebral, local and segmental kyphosis of traumatic lumbar spine fractures in the lateral X-ray.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010 Dec;130(12):1533-8. doi: 10.1007/s00402-010-1104-5. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010. PMID: 20424848
-
Reliability of the measurement of thoracolumbar burst fracture kyphosis with Cobb angle, Gardner angle, and sagittal index.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012 Feb;132(2):221-5. doi: 10.1007/s00402-011-1394-2. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012. PMID: 21912925
-
The Conservative Treatment of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Vertebral Fractures.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018 Oct 19;115(42):697-704. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0697. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2018. PMID: 30479250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoporotic Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Vertebrae: Diagnosis and Conservative Treatment.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021 Oct 8;118(40):670-677. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0295. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021. PMID: 34342263 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology Treatment Options for Osteoporosis and Its Corresponding Consequences.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016 Oct;14(5):239-47. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0324-1. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016. PMID: 27542011 Review.
-
Patient-reported outcomes 1 and 2 years after transforaminal thoracic interbody fusion (TTIF).Eur Spine J. 2024 Mar;33(3):1089-1097. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08042-3. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 37987852
-
Minimally Invasive Stent Screw-Assisted Internal Fixation Technique Corrects Kyphosis in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures with Severe Collapse: A Pilot "Vertebra Plana" Series.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022 May;43(5):776-783. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7493. Epub 2022 Apr 21. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022. PMID: 35450859 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the Cobb angle with the iPhone in kyphoses: a reliability study.Int Orthop. 2012 Aug;36(8):1655-60. doi: 10.1007/s00264-012-1579-5. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Int Orthop. 2012. PMID: 22653103 Free PMC article.
-
Satisfactory 2-year outcome of minimal invasive hybrid stabilization with double treated screws for unstable osteoporotic spinal fractures.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Oct;50(5):2385-2398. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02645-1. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 39212727 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical