Nanobiocatalysis for protein digestion in proteomic analysis
- PMID: 19953546
- PMCID: PMC2908020
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200900519
Nanobiocatalysis for protein digestion in proteomic analysis
Abstract
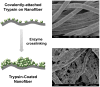
The process of protein digestion is a critical step for successful protein identification in bottom-up proteomic analyses. To substitute the present practice of in-solution protein digestion, which is long, tedious, and difficult to automate, many efforts have been dedicated for the development of a rapid, recyclable and automated digestion system. Recent advances of nanobiocatalytic approaches have improved the performance of protein digestion by using various nanomaterials such as nanoporous materials, magnetic nanoparticles, and polymer nanofibers. Especially, the unprecedented success of trypsin stabilization in the form of trypsin-coated nanofibers, showing no activity decrease under repeated uses for 1 year and retaining good resistance to proteolysis, has demonstrated its great potential to be employed in the development of automated, high-throughput, and on-line digestion systems. This review discusses recent developments of nanobiocatalytic approaches for the improved performance of protein digestion in speed, detection sensitivity, recyclability, and trypsin stability. In addition, we also introduce approaches for protein digestion under unconventional energy input for protein denaturation and the development of microfluidic enzyme reactors that can benefit from recent successes of these nanobiocatalytic approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kim J, Grate JW, Wang P. Nanobiocatalysis and its potential applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2008;26:639–646. - PubMed
-
- Mouradian S. Lab-on-a-chip: applications in proteomics. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002;6:51–56. - PubMed
-
- Kim J, Grate JW, Wang P. Nanostructures for enzyme stabilization. Chem Eng Sci. 2006;61:1017–1026.
-
- Kim J, Jia HF, Wang P. Challenges in biocatalysis for enzyme-based biofuel cells. Biotechnol Adv. 2006;24:296–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

