Identification of a novel "almost neutral" micro-opioid receptor antagonist in CHO cells expressing the cloned human mu-opioid receptor
- PMID: 19953652
- PMCID: PMC2821452
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20723
Identification of a novel "almost neutral" micro-opioid receptor antagonist in CHO cells expressing the cloned human mu-opioid receptor
Abstract
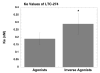
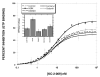
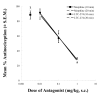
The basal (constitutive) activity of G protein-coupled receptors allows for the measurement of inverse agonist activity. Some competitive antagonists turn into inverse agonists under conditions where receptors are constitutively active. In contrast, neutral antagonists have no inverse agonist activity, and they block both agonist and inverse agonist activity. The mu-opioid receptor (MOR) demonstrates detectable constitutive activity only after a state of dependence is produced by chronic treatment with a MOR agonist. We therefore sought to identify novel MOR inverse agonists and novel neutral MOR antagonists in both untreated and agonist-treated MOR cells. CHO cells expressing the cloned human mu receptor (hMOR-CHO cells) were incubated for 20 h with medium (control) or 10 microM (2S,4aR,6aR,7R,9S,10aS,10bR)-9-(benzoyloxy)-2-(3-furanyl)dodecahydro-6a,10b-dimethyl-4,10-dioxo-2H-naphtho-[2,1-c]pyran-7-carboxylic acid methyl ester (herkinorin, HERK). HERK treatment generates a high degree of basal signaling and enhances the ability to detect inverse agonists. [(35)S]-GTP-gamma-S assays were conducted using established methods. We screened 21 MOR "antagonists" using membranes prepared from HERK-treated hMOR-CHO cells. All antagonists, including CTAP and 6beta-naltrexol, were inverse agonists. However, LTC-274 ((-)-3-cyclopropylmethyl-2,3,4,4alpha,5,6,7,7alpha-octahydro-1H-benzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-9-ol)) showed the lowest efficacy as an inverse agonist, and, at concentrations less than 5 nM, had minimal effects on basal [(35)S]-GTP-gamma-S binding. Other efforts in this study identified KC-2-009 ((+)-3-((1R,5S)-2-((Z)-3-phenylallyl)-2-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonan-5-yl)phenol hydrochloride) as an inverse agonist at untreated MOR cells. In HERK-treated cells, KC-2-009 had the highest efficacy as an inverse agonist. In summary, we identified a novel and selective MOR inverse agonist (KC-2-009) and a novel MOR antagonist (LTC-274) that shows the least inverse agonist activity among 21 MOR antagonists. LTC-274 is a promising lead compound for developing a true MOR neutral antagonist.
Figures

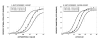
References
-
- Bilsky EJ, Bernstein RN, Wang Z, Sadee W, Porreca F. Effects of naloxone and D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Arg-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2 and the protein kinase inhibitors H7 and H8 on acute morphine dependence and antinociceptive tolerance in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996;277:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Ciganek E. 2,3,4,4a,5,6,7,7a-Octahydro-1H-benzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline: a new morphine fragment. J Am Chem Soc. 1981;103(20):6261–6262.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
