Abscess of adrenal gland caused by disseminated subacute Nocardia farcinica pneumonia. A case report and mini-review of the literature
- PMID: 19954528
- PMCID: PMC2792227
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-194
Abscess of adrenal gland caused by disseminated subacute Nocardia farcinica pneumonia. A case report and mini-review of the literature
Abstract
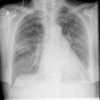
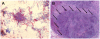
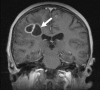
Background: Infections caused by Nocardia farcinica are uncommon and show a great variety of clinical manifestations in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Because of its unspecific symptoms and tendency to disseminate it may mimic the clinical symptoms and radiologic findings of a tumour disease and the diagnosis of nocardiosis can easily be missed, because there are no characteristic symptoms.
Case presentation: We present a case of an adrenal gland abscess caused by subacute disseminated N. farcinica pneumonia.
Conclusion: An infection with N. farcinica is potentially lethal because of its tendency to disseminate -particularly in the brain- and its high resistance to antibiotics. Awareness of this differential diagnosis allows early and appropriate treatment to be administered.
Figures

References
-
- Euzèby J. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature - Genus Nocardia. 2009. http://www.bacterio.cict.fr/n/nocardia.html - PubMed
-
- Roth A, Andrees S, Kroppenstedt RM, Harmsen D, Mauch H. Phylogeny of the genus Nocardia based on reassessed 16S rRNA gene sequences reveals underspeciation and division of strains classified as Nocardia asteroides into three established species and two unnamed taxons. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41(2):851–856. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.2.851-856.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cloud JL, Conville PS, Croft A, Harmsen D, Witebsky FG, Carroll KC. Evaluation of partial 16S ribosomal DNA sequencing for identification of nocardia species by using the MicroSeq 500 system with an expanded database. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42(2):578–584. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.2.578-584.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

