Nano/Microfluidics for diagnosis of infectious diseases in developing countries
- PMID: 19954755
- PMCID: PMC2829381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.016
Nano/Microfluidics for diagnosis of infectious diseases in developing countries
Abstract
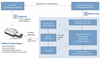
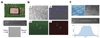
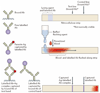
Nano/Microfluidic technologies are emerging as powerful enabling tools for diagnosis and monitoring of infectious diseases in both developed and developing countries. Miniaturized nano/microfluidic platforms that precisely manipulate small fluid volumes can be used to enable medical diagnosis in a more rapid and accurate manner. In particular, these nano/microfluidic diagnostic technologies are potentially applicable to global health applications, since they are disposable, inexpensive, portable, and easy-to-use for detection of infectious diseases. In this paper, we review recent advances in nano/microfluidic technologies for clinical point-of-care applications at resource-limited settings in developing countries.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Yager P, Edwards T, Fu E, Helton K, Nelson K, Tam MR, Weigl BH. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature. 2006;442:412–418. - PubMed
-
- Urdea M, Penny LA, Olmsted SS, Giovanni MY, Kaspar P, Shepherd A, Wilson P, Dahl CA, Buchsbaum S, Moeller G, Hay DC. Burgess, Requirements for high impact diagnostics in the developing world. Nature. 2006;444 Suppl 1:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Yager P, Domingo GJ, Gerdes J. Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2008;10:107–144. - PubMed
-
- Mabey D, Peeling RW, Ustianowski A, Perkins MD. Diagnostics for the developing world. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:231–240. - PubMed
-
- Hay Burgess DC, Wasserman J, Dahl CA. Global health diagnostics. Nature. 2006;444 Suppl 1:1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

