Human T cell lymphotropic virus 1 manipulates interferon regulatory signals by controlling the TAK1-IRF3 and IRF4 pathways
- PMID: 19955181
- PMCID: PMC2836049
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.031476
Human T cell lymphotropic virus 1 manipulates interferon regulatory signals by controlling the TAK1-IRF3 and IRF4 pathways
Abstract
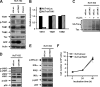
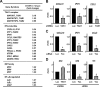
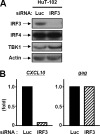
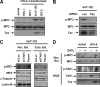
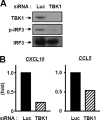
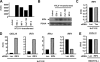
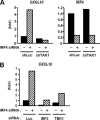
We previously reported that human T cell lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1) Tax oncoprotein constitutively activates transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1). Here, we established Tax-positive HuT-102 cells stably transfected with a short hairpin RNA vector (HuT-shTAK1 cells) and investigated the physiological function of TAK1. Microarray analysis demonstrated that several interferon (IFN)-inducible genes, including chemokines such as CXCL10 and CCL5, were significantly down-regulated in HuT-shTAK1 cells. In contrast, Tax-mediated constitutive activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) was intact in HuT-shTAK1 cells. IFN-regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), a critical transcription factor in innate immunity to viral infection, was constitutively activated in a Tax-dependent manner. Activation of IRF3 and IRF3-dependent gene expressions was dependent on TAK1 and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1). On the other hand, IRF4, another member in the IRF family of transcription factors overexpressed in a Tax-independent manner, negatively regulated TAK1-dependent IRF3 transcriptional activity. Together, HTLV-1 manipulates IFN signaling by regulating both positive and negative IRFs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of Type I Interferon Production by Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Oncoprotein Tax through Inhibition of IRF3 Phosphorylation.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):3902-3912. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00129-16. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26819312 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-c-Rel and interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) pathways in human T cell lymphotropic virus 1-transformed T helper 17 cells producing interleukin-9.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21092-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.200907. Epub 2011 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21498517 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1 Tax-mediated TAK1 activation involves TAB2 adapter protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Jan 4;365(1):189-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.10.172. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 17986383
-
Activation of I-kappaB kinase by the HTLV type 1 Tax protein: mechanistic insights into the adaptor function of IKKgamma.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 Nov 1;16(16):1591-6. doi: 10.1089/08892220050193001. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 11080796 Review.
-
Persistent activation of NF-kappaB by the tax transforming protein of HTLV-1: hijacking cellular IkappaB kinases.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6948-58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203220. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602469 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Type I Interferon Production by Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Oncoprotein Tax through Inhibition of IRF3 Phosphorylation.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):3902-3912. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00129-16. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26819312 Free PMC article.
-
Positive and Negative Regulation of Type I Interferons by the Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Antisense Protein HBZ.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00853-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00853-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768861 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-α (IFN-α) suppresses HTLV-1 gene expression and cell cycling, while IFN-α combined with zidovudine induces p53 signaling and apoptosis in HTLV-1-infected cells.Retrovirology. 2013 May 20;10:52. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-52. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 23688327 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopathogenesis and Cellular Interactions in Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Dec 22;11:614940. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.614940. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33414779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRKX down-regulates TAK1/IRF7 signaling in the antiviral innate immunity of black carp Mylopharyngodon piceus.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 11;13:999219. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.999219. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Honda K., Takaoka A., Taniguchi T. (2006) Immunity 25, 349–360 - PubMed
-
- Sato M., Suemori H., Hata N., Asagiri M., Ogasawara K., Nakao K., Nakaya T., Katsuki M., Noguchi S., Tanaka N., Taniguchi T. (2000) Immunity 13, 539–548 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald K. A., McWhirter S. M., Faia K. L., Rowe D. C., Latz E., Golenbock D. T., Coyle A. J., Liao S. M., Maniatis T. (2003) Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 - PubMed
-
- Sharma S., tenOever B. R., Grandvaux N., Zhou G. P., Lin R., Hiscott J. (2003) Science 300, 1148–1151 - PubMed
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. (2007) J. Biochem. 141, 137–145 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

