PYK2 interacts with MyD88 and regulates MyD88-mediated NF-kappaB activation in macrophages
- PMID: 19955209
- PMCID: PMC2830122
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0309125
PYK2 interacts with MyD88 and regulates MyD88-mediated NF-kappaB activation in macrophages
Abstract
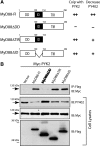
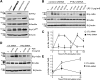
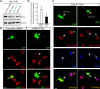
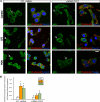
PYK2, a major cell adhesion-activated tyrosine kinase, is highly expressed in macrophages and implicated in macrophage activation and inflammatory response. However, mechanisms by which PYK2 regulates inflammatory response are beginning to be understood. In this study, we demonstrate that PYK2 interacts with MyD88, a crucial signaling adaptor protein in LPS and PGN-induced NF-kappaB activation, in vitro and in macrophages. This interaction, increased in macrophages, stimulated by LPS, requires the death domain of MyD88. PYK2-deficient macrophages exhibit reduced phosphorylation and degradation of IkappaB, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation, and decreased NF-kappaB activation and IL-1beta expression by LPS. These results suggest that via interaction with MyD88, PYK2 is involved in modulating cytokine (e.g., LPS) stimulation of NF-kappaB activity and signaling, providing a mechanism underlying PYK2 regulation of an inflammatory response.
Figures


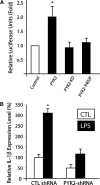
References
-
- Li X, Qin J. Modulation of Toll-interleukin 1 receptor mediated signaling. J Mol Med. 2005;83:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Davidson D J, Currie A J, Bowdish D M, Brown K L, Rosenberger C M, Ma R C, Bylund J, Campsall P A, Puel A, Picard C, Casanova J L, Turvey S E, Hancock R E, Devon R S, Speert D P. IRAK-4 mutation (Q293X): rapid detection and characterization of defective post-transcriptional TLR/IL-1R responses in human myeloid and non-myeloid cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:8202–8211. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Neill L A, Bowie A G. The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:353–364. - PubMed
-
- Rakoff-Nahoum S, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Moynagh P N. The Pellino family: IRAK E3 ligases with emerging roles in innate immune signaling. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

