Deep brain stimulation does not silence neurons in subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's patients
- PMID: 19955287
- PMCID: PMC3141810
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00363.2009
Deep brain stimulation does not silence neurons in subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson's patients
Abstract
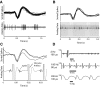
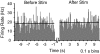
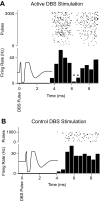
Two broad hypotheses have been advanced to explain the clinical efficacy of deep brain stimulation (DBS) in the subthalamic nucleus (STN) for treatment of Parkinson's disease. One is that stimulation inactivates STN neurons, producing a functional lesion. The other is that electrical stimulation activates the STN output, thus "jamming" pathological activity in basal ganglia-corticothalamic circuits. Evidence consistent with both concepts has been adduced from modeling and animal studies, as well as from recordings in patients. However, the stimulation parameters used in many recording studies have not been well matched to those used clinically. In this study, we recorded STN activity in patients with Parkinson's disease during stimulation delivered through a clinical DBS electrode using standard therapeutic stimulus parameters. A microelectrode was used to record the firing of a single STN neuron during DBS (3-5 V, 80-200 Hz, 90- to 200-micros pulses; 33 neurons/11 patients). Firing rate was unchanged during the stimulus trains, and the recorded neurons did not show prolonged (s) changes in firing rate on termination of the stimulation. However, a brief (approximately 1 ms), short-latency (6 ms) postpulse inhibition was seen in 10 of 14 neurons analyzed. A subset of neurons displayed altered firing patterns, with a predominant shift toward random firing. These data do not support the idea that DBS inactivates the STN and are instead more consistent with the hypothesis that this stimulation provides a null signal to basal ganglia-corticothalamic circuitry that has been altered as part of Parkinson's disease.
Figures


References
-
- Albin RL, Young A, Penny JB. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12: 366–375, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL, Chabardes S, Mitrofanis J, Pollak P. Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 8: 67–81, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bronte-Stewart H, Barberini C, Koop MM, Hill BC, Henderson JM, Wingeier B. The STN beta-band profile in Parkinson's disease is stationary and shows prolonged attenuation after deep brain stimulation. Exp Neurol 215: 20–28, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease Study Group Deep-brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus or the pars interna of the globus pallidus in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 345: 956–963, 2001 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

