Interneurons produced in adulthood are required for the normal functioning of the olfactory bulb network and for the execution of selected olfactory behaviors
- PMID: 19955377
- PMCID: PMC6665973
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3606-09.2009
Interneurons produced in adulthood are required for the normal functioning of the olfactory bulb network and for the execution of selected olfactory behaviors
Abstract
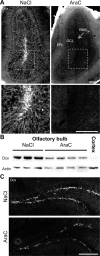
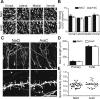
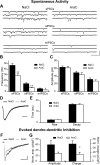
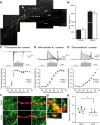
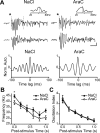
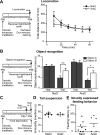
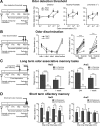
Olfactory bulb (OB) interneurons are continuously renewed throughout an animal's lifespan. Despite extensive investigation of this phenomenon, little is known about bulbar circuitry functioning and olfactory performances under conditions of ablated arrival of new neurons into the adult OB. To address this issue we performed morphological, electrophysiological, and behavioral analysis in mice with suppressed bulbar neurogenesis. Infusion of the antimitotic drug AraC to the lateral ventricle via 28 d osmotic minipumps abolished the arrival of newly born neurons into the adult OB without affecting the total number of granule cells. The number, dendritic arborization, and spine density of interneurons generated in adulthood, before pump installation, were also not affected by AraC treatment. As a result of ablated neurogenesis, mitral cells--the principal output neurons in the OB--receive fewer inhibitory synapses, display reduced frequency of spontaneous IPSCs, experience smaller dendrodendritic inhibition, and exhibit decreased synchronized activity. Consequently, short-term olfactory memory was drastically reduced in AraC-treated mice. In contrast, olfactory performances of AraC-treated animals were undistinguishable from those of control mice in other odor-associated tests, such as spontaneous odor discrimination and long-term odor-associative memory tasks. Altogether, our data highlight the importance of adult neurogenesis for the proper functioning of the OB network and imply that new bulbar interneurons are involved in some, but not all, odor-associated tasks.
Figures
Comment in
-
Functional contribution of adult-generated olfactory bulb interneurons: odor discrimination versus odor memory.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 31;30(13):4523-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0443-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20357101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Barkai E, Saar D. Cellular correlates of olfactory learning in the rat piriform cortex. Rev Neurosci. 2001;12:111–120. - PubMed
-
- Bevins RA, Besheer J. Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trial non-matching-to-sample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:1306–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
