ApoE4 decreases spine density and dendritic complexity in cortical neurons in vivo
- PMID: 19955384
- PMCID: PMC2846754
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4026-09.2009
ApoE4 decreases spine density and dendritic complexity in cortical neurons in vivo
Abstract
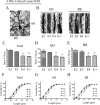
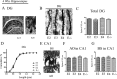
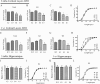
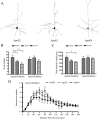
The three human alleles of apolipoprotein E (APOE) differentially influence outcome after CNS injury and affect one's risk of developing Alzheimer's disease (AD). It remains unclear how ApoE isoforms contribute to various AD-related pathological changes (e.g., amyloid plaques and synaptic and neuron loss). Here, we systematically examined whether apoE isoforms (E2, E3, E4) exhibit differential effects on dendritic spine density and morphology in APOE targeted replacement (TR) mice, which lack AD pathological changes. Using Golgi staining, we found age-dependent effects of APOE4 on spine density in the cortex. The APOE4 TR mice had significantly reduced spine density at three independent time points (4 weeks, 3 months, and 1 year, 27.7% +/- 7.4%, 24.4% +/- 8.6%, and 55.6% +/- 10.5%, respectively) compared with APOE3 TR mice and APOE2 TR mice. Additionally, in APOE4 TR mice, shorter spines were evident compared with other APOE TR mice at 1 year. APOE2 TR mice exhibited longer spines as well as significantly increased apical dendritic arborization in the cortex compared with APOE4 and APOE3 TR mice at 4 weeks. However, there were no differences in spine density across APOE genotypes in hippocampus. These findings demonstrate that apoE isoforms differentially affect dendritic complexity and spine formation, suggesting a role for APOE genotypes not only in acute and chronic brain injuries including AD, but also in normal brain functions.
Figures
Comment in
-
Differential effects of ApoE isoforms on dendritic spines in vivo: linking an Alzheimer's disease risk factor with synaptic alterations.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 31;30(13):4526-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0505-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20357102 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alpár A, Ueberham U, Brückner MK, Seeger G, Arendt T, Gärtner U. Different dendrite and dendritic spine alterations in basal and apical arbors in mutant human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Brain Res. 2006;1099:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Bellosta S, Nathan BP, Orth M, Dong LM, Mahley RW, Pitas RE. Stable expression and secretion of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 in mouse neuroblastoma cells produces differential effects on neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27063–27071. - PubMed
-
- Daniele A, Matera MG, Seripa D, Acciarri A, Bizzarro A, Pilotto A, Masullo C. APOE ε2/ε4 genotype a risk factor for primary progressive aphasia in women. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:910–912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
