Estradiol-induced estrogen receptor-alpha trafficking
- PMID: 19955385
- PMCID: PMC2836237
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2107-09.2009
Estradiol-induced estrogen receptor-alpha trafficking
Abstract
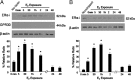
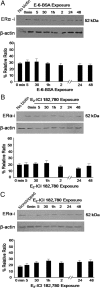
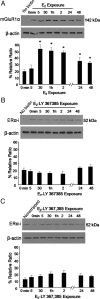
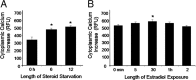
Estradiol has rapid actions in the CNS that are mediated by membrane estrogen receptors (ERs) and activate cell signaling pathways through interaction with metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). Membrane-initiated estradiol signaling increases the free cytoplasmic calcium concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) that stimulates the synthesis of neuroprogesterone in astrocytes. We used surface biotinylation to demonstrate that ERalpha has an extracellular portion. In addition to the full-length ERalpha [apparent molecular weight (MW), 66 kDa], surface biotinylation labeled an ERalpha-immunoreactive protein (MW, approximately 52 kDa) identified by both COOH- and NH(2)-directed antibodies. Estradiol treatment regulated membrane levels of both proteins in parallel: within 5 min, estradiol significantly increased membrane levels of the 66 and 52 kDa ERalpha. Internalization, a measure of membrane receptor activation, was also increased by estradiol with a similar time course. Continuous treatment with estradiol for 24-48 h reduced ERalpha levels, suggesting receptor downregulation. Estradiol also increased mGluR1a trafficking and internalization, consistent with the proposed ERalpha-mGluR1a interaction. Blocking ER with ICI 182,780 or mGluR1a with LY 367385 prevented ERalpha trafficking to and from the membrane. Estradiol-induced [Ca(2+)](i) flux was also significantly increased at the time of peak ERalpha activation/internalization. These results demonstrate that ERalpha is present in the membrane and has an extracellular portion. Furthermore, membrane levels and internalization of ERalpha are regulated by estradiol and mGluR1a ligands. The pattern of trafficking into and out of the membrane suggests that the changing concentration of estradiol during the estrous cycle regulates ERalpha to augment and then terminate membrane-initiated signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Azcoitia I, Sierra A, Garcia-Segura LM. Localization of estrogen receptor beta-immunoreactivity in astrocytes of the adult rat brain. Glia. 1999;26:260–267. - PubMed
-
- Beyer C, Pawlak J, Karolczak M. Membrane receptors for oestrogen in the brain. J Neurochem. 2003;87:545–550. - PubMed
-
- Bollig A, Miksicek RJ. An estrogen receptor-alpha splicing variant mediates both positive and negative effects on gene transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:634–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
