IL-17-producing T cells can augment autoantibody-induced arthritis
- PMID: 19955422
- PMCID: PMC2799826
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0912152106
IL-17-producing T cells can augment autoantibody-induced arthritis
Abstract
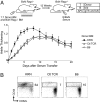
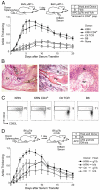
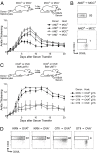
Rheumatoid arthritis is a T lymphocyte-mediated disorder, but the precise nature of T cell involvement remains unclear. In the K/BxN mouse model of inflammatory arthritis, T cells initiate disease by providing help to B cells to produce arthritogenic autoantibodies. Here, we have characterized an additional, nonhumoral role for T cells in promoting autoantibody-induced arthritis. Autoreactive KRN T cells introduced either by direct transfer or bone marrow transplantation into B-cell-deficient hosts enhanced K/BxN serum-transferred arthritis, an effect that was dependent on expression of the cognate MHC-molecule/peptide complex. The T cell influence was dependent on interleukin (IL)-17; in contrast, standard serum-transferred arthritis, unenhanced by the addition of T cells, was unaffected by IL-17 neutralization. An IL-17-producing population of transferred KRN T cells was identified and found to be supported by the cotransfer of arthritogenic autoantibodies. IL-17-producing KRN T cells were enriched in inflamed joints of K/BxN mice, suggesting either selective recruitment or preferential differentiation. These results demonstrate the potential for autoreactive T cells to play two roles in the development of arthritis, both driving the production of pathogenic autoantibodies and bolstering the subsequent inflammatory cascade dependent on the innate immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
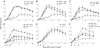

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

