2,2,2-trichloroethanol activates a nonclassical potassium channel in cerebrovascular smooth muscle and dilates the middle cerebral artery
- PMID: 19955488
- PMCID: PMC2835435
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.162313
2,2,2-trichloroethanol activates a nonclassical potassium channel in cerebrovascular smooth muscle and dilates the middle cerebral artery
Abstract
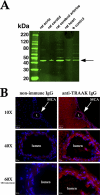
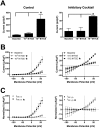
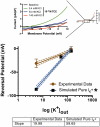
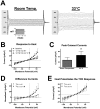
Trichloroacetaldehyde monohydrate [chloral hydrate (CH)] is a sedative/hypnotic that increases cerebral blood flow (CBF), and its active metabolite 2,2,2-trichloroethanol (TCE) is an agonist for the nonclassical two-pore domain K(+) (K(2P)) channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. We sought to determine whether TCE dilates cerebral arteries in vitro by activating nonclassical K(+) channels. TCE dilated pressurized and perfused rat middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) in a manner consistent with activation of nonclassical K(+) channels. Dilation to TCE was inhibited by elevated external K(+) but not by an inhibitory cocktail (IC) of classical K(+) channel blockers. Patch-clamp electrophysiology revealed that, in the presence of the IC, TCE increased whole-cell currents and hyperpolarized the membrane potential of isolated MCA smooth muscle cells. Heating increased TCE-sensitive currents, indicating that the activated channel was thermosensitive. Immunofluorescence in sections of the rat MCA demonstrated that, like TREK-1, TRAAK is expressed in the smooth muscle of cerebral arteries. Isoflurane did not, however, dilate the MCA, suggesting that TREK-1 was not functional. These data indicate that TCE activated a nonclassical K(+) channel with the characteristics of TRAAK in rat MCA smooth-muscle cells. Stimulation of K(+) channels such as TRAAK in cerebral arteries may therefore explain in part how CH/TCE increases CBF.
Figures
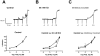


References
-
- Andresen JJ, Shafi NI, Durante W, Bryan RM., Jr (2006) Effects of carbon monoxide and heme oxygenase inhibitors in cerebral vessels of rats and mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H223–H230 - PubMed
-
- Beland FA. (1999) NTP technical report on the toxicity and metabolism studies of chloral hydrate (CAS No. 302-17-0). Administered by gavage to F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Toxic Rep Ser 1–66, A61–E67 - PubMed
-
- Blondeau N, Pétrault O, Manta S, Giordanengo V, Gounon P, Bordet R, Lazdunski M, Heurteaux C. (2007) Polyunsaturated fatty acids are cerebral vasodilators via the TREK-1 potassium channel. Circ Res 101:176–184 - PubMed
-
- Bryan RM, Jr, You J, Phillips SC, Andresen JJ, Lloyd EE, Rogers PA, Dryer SE, Marrelli SP. (2006) Evidence for two-pore domain potassium channels in rat cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H770–H780 - PubMed
-
- Cabana BE, Gessner PK. (1970) The kinetics of chloral hydrate metabolism in mice and the effect thereon of ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 174:260–275 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

