Rapid enhancement of glutamatergic neurotransmission in bipolar depression following treatment with riluzole
- PMID: 19956089
- PMCID: PMC3055603
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2009.191
Rapid enhancement of glutamatergic neurotransmission in bipolar depression following treatment with riluzole
Abstract
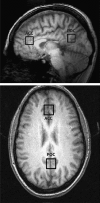
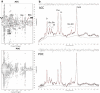
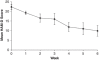
Glutamatergic abnormalities may underlie bipolar disorder (BD). The glutamate-modulating drug riluzole may be efficacious in bipolar depression, but few in vivo studies have examined its effect on glutamatergic neurotransmission. We conducted an exploratory study of the effect of riluzole on brain glutamine/glutamate (Gln/Glu) ratios and levels of N-acetylaspartate (NAA). We administered open-label riluzole 100-200 mg daily for 6 weeks to 14 patients with bipolar depression and obtained imaging data from 8-cm(3) voxels in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and parieto-occipital cortex (POC) at baseline, day 2, and week 6 of treatment, using two-dimensional J-resolved proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 4 T. Imaging data were analyzed using the spectral-fitting package, LCModel; statistical analysis used random effects mixed models. Riluzole significantly reduced Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) scores (d=3.4; p<0.001). Gln/Glu ratios increased significantly by day 2 of riluzole treatment (Cohen's d=1.2; p=0.023). NAA levels increased significantly from baseline to week 6 (d=1.2; p=0.035). Reduction in HAM-D scores was positively associated with increases in NAA from baseline to week 6 in the ACC (d=1.4; p=0.053), but was negatively associated in the POC (d=9.6; p<0.001). Riluzole seems to rapidly increase Gln/Glu ratios-suggesting increased glutamate-glutamine cycling, which may subsequently enhance neuronal plasticity and reduce depressive symptoms. Further investigation of the Gln/Glu ratio as a possible early biomarker of response to glutamate-modulating therapies is warranted.
Figures




References
-
- Banasr M, Chowdhury GM, Terwilliger R, Newton SS, Duman RS, Behar KL, et al. 2008Glial pathology in an animal model of depression: reversal of stress-induced cellular, metabolic and behavioral deficits by the glutamate-modulating drug riluzole Mol Psychiatry(e-pub ahead of print 30 September). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batra NA, Seres-Mailo J, Hanstock C, Seres P, Khudabux J, Bellavance F, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy measurement of brain glutamate levels in premenstrual dysphoric disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:1178–1184. - PubMed
-
- Bhagwagar Z, Wylezinska M, Jezzard P, Evans J, Ashworth F, Sule A, et al. Reduction in occipital cortex gamma-aminobutyric acid concentrations in medication-free recovered unipolar depressed and bipolar subjects. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:806–812. - PubMed
-
- Cecil KM, DelBello MP, Morey R, Strakowski SM. Frontal lobe differences in bipolar disorder as determined by proton MR spectroscopy. Bipolar Disord. 2002;4:357–365. - PubMed
-
- Cheramy A, Barbeito L, Godeheu G, Glowinski J. Riluzole inhibits the release of glutamate in the caudate nucleus of the cat in vivo. Neurosci Lett. 1992;147:209–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

