Interventions to promote cancer awareness and early presentation: systematic review
- PMID: 19956160
- PMCID: PMC2790702
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605388
Interventions to promote cancer awareness and early presentation: systematic review
Abstract
Background: Low cancer awareness contributes to delay in presentation for cancer symptoms and may lead to delay in cancer diagnosis. The aim of this study was to review the evidence for the effectiveness of interventions to raise cancer awareness and promote early presentation in cancer to inform policy and future research.
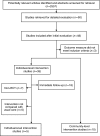
Methods: We searched bibliographic databases and reference lists for randomised controlled trials of interventions delivered to individuals, and controlled or uncontrolled studies of interventions delivered to communities.
Results: We found some evidence that interventions delivered to individuals modestly increase cancer awareness in the short term and insufficient evidence that they promote early presentation. We found limited evidence that public education campaigns reduce stage at presentation of breast cancer, malignant melanoma and retinoblastoma.
Conclusions: Interventions delivered to individuals may increase cancer awareness. Interventions delivered to communities may promote cancer awareness and early presentation, although the evidence is limited.
References
-
- Boundouki G, Humphris G, Field A (2004) Knowledge of oral cancer, distress and screening intentions: longer term effects of a patient information leaflet. Patient Educ Couns 53: 71–77 - PubMed
-
- Catalano R, Winett L, Wallack L, Satariano W (2003) Evaluating a campaign to detect early stage breast tumors in the United States. Eur J Epidemiol 18: 545–550 - PubMed
-
- De Nooijer J, Lechner L, Candel M, de Vries H (2004) Short- and long-term effects of tailored information versus general information on determinants and intentions related to early detection of cancer. Prev Med 38: 694–703 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources