Anti-lipopolysaccharide factors in the American lobster Homarus americanus: molecular characterization and transcriptional response to Vibrio fluvialis challenge
- PMID: 19956341
- PMCID: PMC2612121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbd.2008.07.001
Anti-lipopolysaccharide factors in the American lobster Homarus americanus: molecular characterization and transcriptional response to Vibrio fluvialis challenge
Abstract
Two partial mRNA sequences predicted to encode anti-lipopolysaccharide factors (ALFs) were identified among expressed sequence tags generated from the American lobster Homarus americanus and complete cDNA sequences were obtained from library clones. Comparison of the translated amino acid sequences to those publicly available confirmed similarity to arthropod anti-lipopolysaccharide factors. Both protein sequences, designated ALFHa-1 and ALFHa-2, contained an N-terminal signal peptide and two half-cysteines participating in a disulfide bridge, features conserved in other ALFs. Predicted secondary structures were similar to that described for the ALF from the horseshoe crab Limulus polyphemus. As part of an exploratory study of immunity in H. americanus, lobsters were injected with the bacterium Vibrio fluvialis and gill, hematopoietic, and hepatopancreas tissues were sampled for analysis of gene expression of ALFHa-1 and ALFHa-2 by quantitative PCR. The relative abundance of ALFHa-2 mRNA was not significantly affected by Vibrio injection in any of the three tissues tested. In contrast, ALFHa-1 mRNA levels in gills were increased by the treatment some 17-fold. Our results support a molecularly specific regulation of antimicrobial proteins in response to bacterial infection in H. americanus.
Keywords: DNA sequencing; antimicrobial peptides; crustacean; gill tissue; hematopoetic tissue; hepatopancreas tissue; real-time quantitative PCR.
2008 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


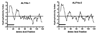




References
-
- Aketagawa J, Miyata T, Ohtsubo S, Nakamura T, Morita T, Hayashida H, Miyata T, Iwanaga S, Takao T, Shimonishi Y. Primary structure of limulus anticoagulant anti-lipopolysaccharide factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:7357–7365. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;340:783–795. - PubMed
-
- Burnett LE, Holman JD, Jorgensen DD, Ikerd JL, Burnett KG. Immune defense reduces respiratory fitness in Callinectes sapidus, the Atlantic blue crab. Biol. Bull. 2006;211:50–57. - PubMed
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR -- a perspective. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;34:597–601. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

