The membrane proteome of the mouse lens fiber cell
- PMID: 19956408
- PMCID: PMC2786885
The membrane proteome of the mouse lens fiber cell
Abstract
Purpose: Fiber cells of the ocular lens are bounded by a highly specialized plasma membrane. Despite the pivotal role that membrane proteins play in the physiology and pathophysiology of the lens, our knowledge of the structure and composition of the fiber cell plasma membrane remains fragmentary. In the current study, we utilized mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics to provide a comprehensive survey of the mouse lens fiber cell membrane proteome.
Methods: Membranes were purified from young mouse lenses and subjected to MudPIT (Multidimensional protein identification technology) analysis. The resulting proteomic data were analyzed further by reference to publically available microarray databases.
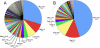
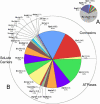
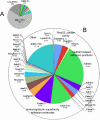
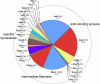
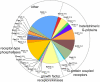
Results: More than 200 membrane proteins were identified by MudPIT, including Type I, Type II, Type III (multi-pass), lipid-anchored, and GPI-anchored membrane proteins, in addition to membrane-associated cytoskeletal elements and extracellular matrix components. The membrane proteins of highest apparent abundance included Mip, Lim2, and the lens-specific connexin proteins Gja3, Gja8, and Gje1. Significantly, many proteins previously unsuspected in the lens were also detected, including proteins with roles in cell adhesion, solute transport, and cell signaling.
Conclusions: The MudPIT technique constitutes a powerful technique for the analysis of the lens membrane proteome and provides valuable insights into the composition of the lens fiber cell unit membrane.
Figures


References
-
- Delamere NA, Tamiya S. Expression, regulation and function of Na,K-ATPase in the lens. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23:593–615. - PubMed
-
- Shiels A, Hejtmancik JF. Genetic origins of cataract. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125:165–73. - PubMed
-
- Shiels A, King JM, Mackay DS, Bassnett S. Refractive defects and cataracts in mice lacking lens intrinsic membrane protein-2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:500–8. - PubMed
-
- Wu CC, MacCoss MJ, Howell KE, Yates JR., 3rd A method for the comprehensive proteomic analysis of membrane proteins. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:532–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
