Triptolide induces anti-inflammatory cellular responses
- PMID: 19956437
- PMCID: PMC2776323
Triptolide induces anti-inflammatory cellular responses
Abstract
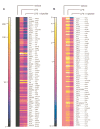
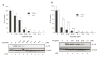
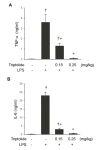
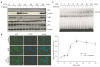
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. has been used for centuries in traditional Chinese medicine to treat rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease associated with increased production of the pro-inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha. Triptolide is a compound originally purified from T. wilfordii Hook F. and has potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant activities. In this study, we investigated the effect of triptolide on the global gene expression patterns of macrophages treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We found that LPS stimulation resulted in >5-fold increase in expression of 117 genes, and triptolide caused a >50% inhibition in 47 of the LPS-inducible 117 genes. A large portion of the genes that were strongly induced by LPS and significantly inhibited by triptolide were pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine genes, including TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6. Interestingly, LPS also induced the expression of micro-RNA-155 (miR-155) precursor, BIC, which was inhibited by triptolide. Confirming the cDNA array results, we demonstrated that triptolide blocked the induction of these pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as miR-155 in a dose-dependent manner. Profound inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression was observed at concentrations as low as 10-50 nM. However, triptolide neither inhibited the phosphorylation or degradation of IkappaBalpha after LPS stimulation, nor affected the DNA-binding activity of NF-kappaB. Surprisingly, we found that triptolide not only inhibited NF-kappaB-regulated reporter transcription, but also dramatically blocked the activity of other transcription factors. Our study offers a plausible explanation of the therapeutic mechanism of T. wilfordii Hook F.
Keywords: Chinese medicine; Inflammation; Tripterygium wilfordii; cytokines; rheumatoid arthritis; transcription.
Figures




References
-
- Chen BJ. Triptolide, a novel immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory agent purified from a Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;42:253–265. - PubMed
-
- Tao X, Cush JJ, Garret M, Lipsky PE. A phase I study of ethyl acetate extract of the chinese antirheumatic herb Tripterygium wilfordii hook F in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2160–2167. - PubMed
-
- Tao X, Younger J, Fan FZ, Wang B, Lipsky PE. Benefit of an extract of Tripterygium Wilfordii Hook F in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1735–1743. - PubMed
-
- Cibere J, Deng Z, Lin Y, Ou R, He Y, Wang Z, Thorne A, Lehman AJ, Tsang IK, Esdaile JM. A randomized double blind, placebo controlled trial of topical Tripterygium wilfordii in rheumatoid arthritis: reanalysis using logistic regression analysis. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:465–467. - PubMed
-
- Qiu D, Kao PN. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active diterpenoid from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. Drugs R D. 2003;4:1–18. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
